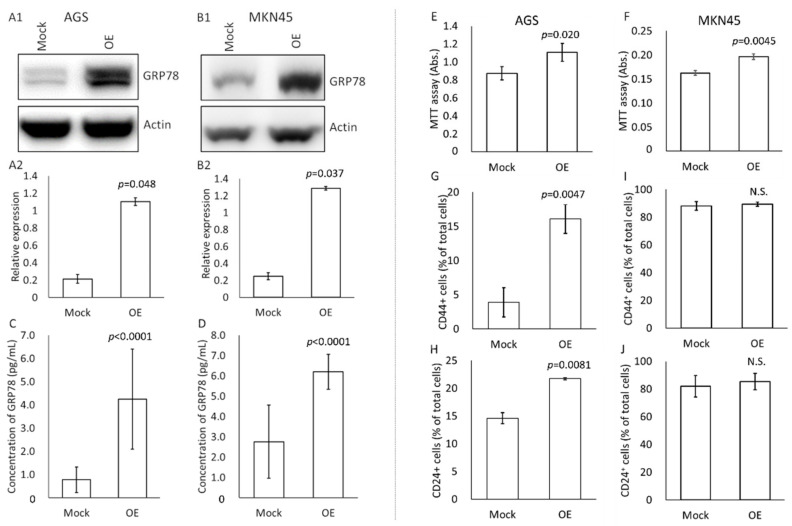
Figure 3.
Effects of the application of GRP78-containing exosomes on changes in profiles of cultured gastric cancer cells. (A,B) Western blotting for GRP78 using cell disruption solutions of AGS (A1) and MKN45 (B1) mock and GRP78-overexpressed (OE) cells. Relative expression levels of GRP78 compared with actin expression in AGS (A2) and MKN45 (B2) mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 3 each. (C) Thio-NAD cycling ELISA for GRP78 in exosomes derived from AGS mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 3 each. (D) Thio-NAD cycling ELISA for GRP78 in exosomes derived from MKN45 mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 4 each. (E) MTT assays for cell viability of AGS cells by application of exosomes isolated from AGS mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 4 each. (F) MTT assays for cell viability of MKN45 cells by application of exosomes isolated from MKN45 mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 3 each. (G,H) Flow cytometry assays (stemness measurements) for (G) CD44-positive and (H) CD24-positive cells in AGS by application of exosomes isolated from AGS mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 3 each. (I,J) Flow cytometry assays (stemness measurements) for (I) CD44-positive and (J) CD24-positive cells in MKN45 cells by application of exosomes isolated from MKN45 mock and GRP78-OE cells. n = 3 each.