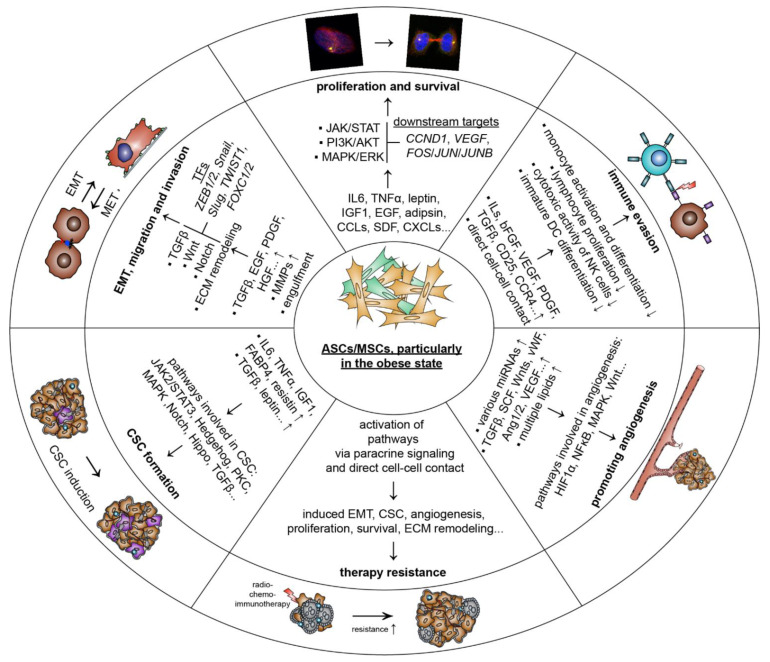
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of potential effect of ASCs/MSCs on breast cancer cells and related molecular mechanisms. ASCs/MSCs may promote breast cancer cell proliferation and survival, EMT, migration, and invasion; CSC formation; angiogenesis; immune evasion; and therapy resistance. ASCs, adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal/stem cells; IL6, interleukin 6; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; ERK, extracellular-signal regulated kinase; IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; CCL2, monocyte chemotactic and activating factor; EGF, epithelial growth factor; PDGF-D, platelet-derived growth factor D; Wnt, wingless/integrated; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; CCR4, C-C motif chemokine receptor 4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; CD25, cluster of differentiation 25; SNAI, snail family transcriptional repressor; ZEB1, zinc finger E-box binding homebox 1; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CSC, cancer stem cell; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; FABP4, fatty acid binding protein 4; PKC, protein kinase C; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; MMP, matrix metalloprotease; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; vWF, von-Willebrand factor.