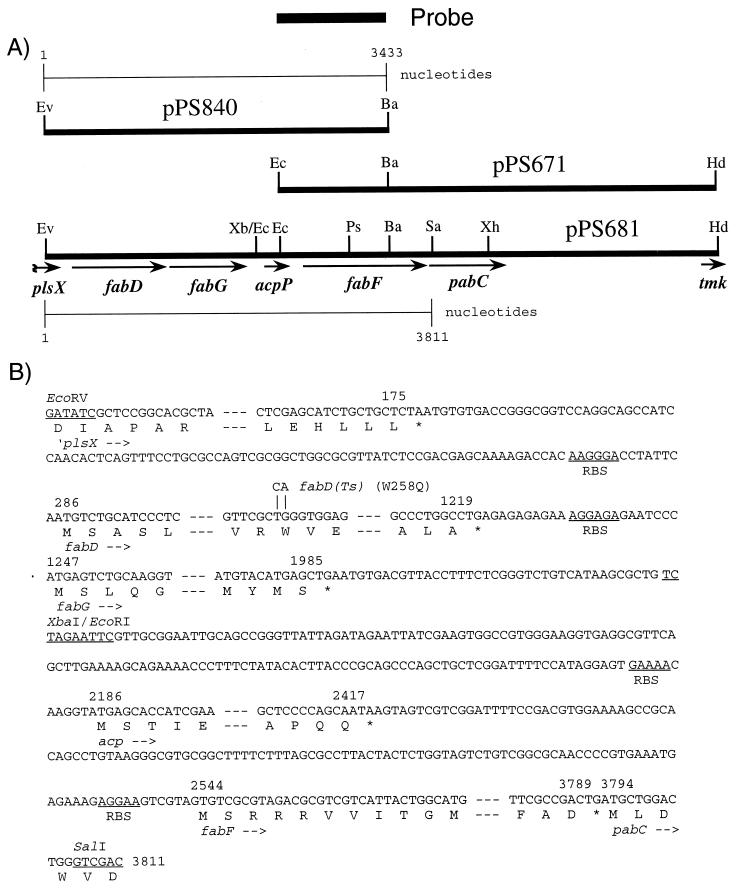
FIG. 1.
The P. aeruginosa acpP region. (A) Maps of plasmids containing a fab gene cluster and flanking genes. The chromosomal inserts of pPS840 and pPS671 were cloned individually, and fusion of these two clones at the common BamHI site yielded pPS681, containing a continuous sequence of this region. Abbreviations: Ba, BamHI; Ec, EcoRI; Ev, EcoRV; Hd, HindIII; Ps, PstI; Sa, SalI; Xb, XbaI; Xh, XhoI. The following genes and their products were identified by nucleotide sequencing: plsX, encoding a poorly understood protein involved in phospholipid biosynthesis; fabD, malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase; fabG, β-ketoacyl-ACP reductase; acpP, ACP; fabF, β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II; pabC, 4-amino-deoxychorismate lyase; tmk, thymidylate kinase. (B) Partial nucleotide sequences of the P. aeruginosa plsX, fabD, fabG, acpP, fabF, and pabC genes. Most of the sequences within the structural genes are omitted, as indicated by dashes. The deduced amino acid sequences are given in one-letter code below the nucleotide sequence. Putative ribosome binding sites (RBS) are labeled. Numbers above the sequence mark the first nucleotides of the initiation and last codons, and stop codons are marked with asterisks. The TG-to-CA nucleotide changes in fabD that were introduced by site-directed mutagenesis and resulted in a W258Q change and a FabD(Ts) phenotype are indicated above the nucleotide sequence.