Table 3.
The imaging configurations and main clinical distinctions of T1w, T2w, ceT1w, and FLAIR.
| Sequence | Sequence Characteristics | Main Clinical Distinctions | Example * |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1w | Uses short TR and TE [64] |
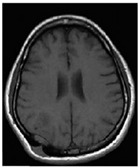
|
|
| T2w | Uses long TR and TE [64] |
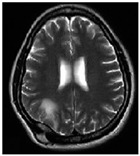
|
|
| ceT1w | Uses the same TR and TE as T1w; employs contrast agents [64] |
|
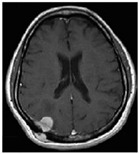
|
| FLAIR | Uses very long TR and TE; the inversion time nulls the signal from fluid [67] |
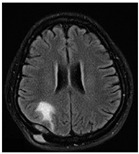
|
* Pictures from [68]. TR, repetition time. TE, echo time.
