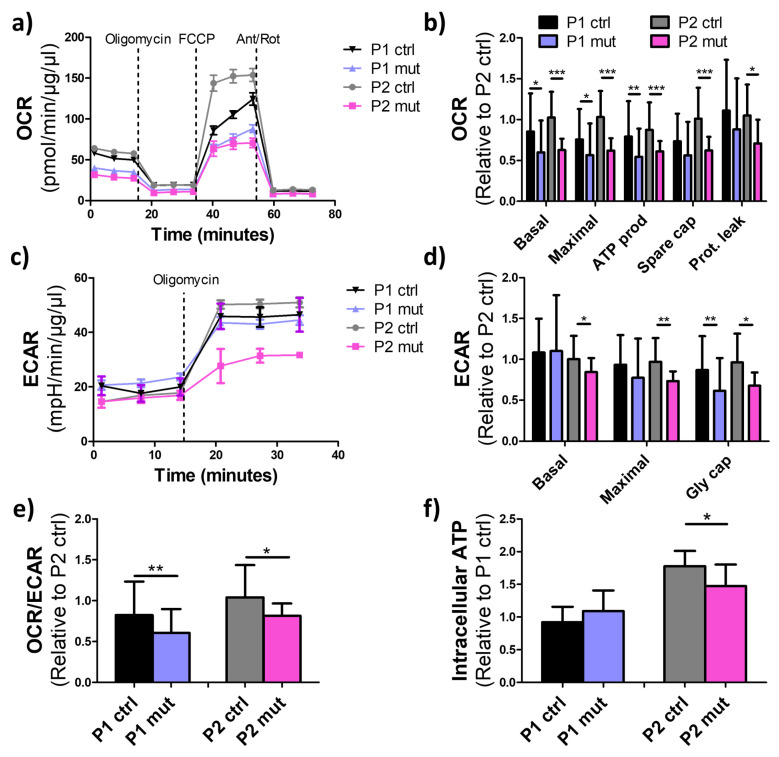
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial respiration is decreased in patient cardiomyocytes upon a high mutation load. (a) Oxygen consumption rates (OCR) at basal level and after inhibition of the RC with oligomycin (CV inhibitor), FCCP (uncoupling agent), and Antimycin A (CIII inhibitor) and Rotenone (CI inhibitor) (Ant/Rot). Data is normalized to total protein content. Respiratory activity is reduced in mutant cells of both patients. (b) Analysis of the OCR data relative to one P1 ctrl line. Prot. Leak = Proton leak. (c) Extra Cellular Acidification Rates (ECAR) at the basal level and after inhibition of mitochondrial ATP synthesis with oligomycin, data normalized to total protein content. The ECAR is reduced in mutant cells of P2, indicating reduced glycolytic activity. (d) Analysis of the ECAR data relative to one P2 ctrl line. Gly cap = glycolytic capacity. (e) OCR/ECAR ratios representing relative oxidative activity calculated at basal level and relative to one P2 ctrl line. (f) Intracellular ATP levels in iPSC-CMs measured with ATPlite assay. Relative to one P1 ctrl line. Cellular ATP levels are reduced upon a high mutation amount in P2 cells. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01 *** p < 0.001. All results are shown as mean +/− SD and calculated from three independent experiments. Mitochondrial respiration analysis: P1 ctrl n = 36, P1 mut n = 38, P2 ctrl n = 74, P2 mut n = 14; ATPlite assay: P1 ctrl n = 20, P1 mut n = 13, P2 ctrl n = 15, P2 mut n = 28.