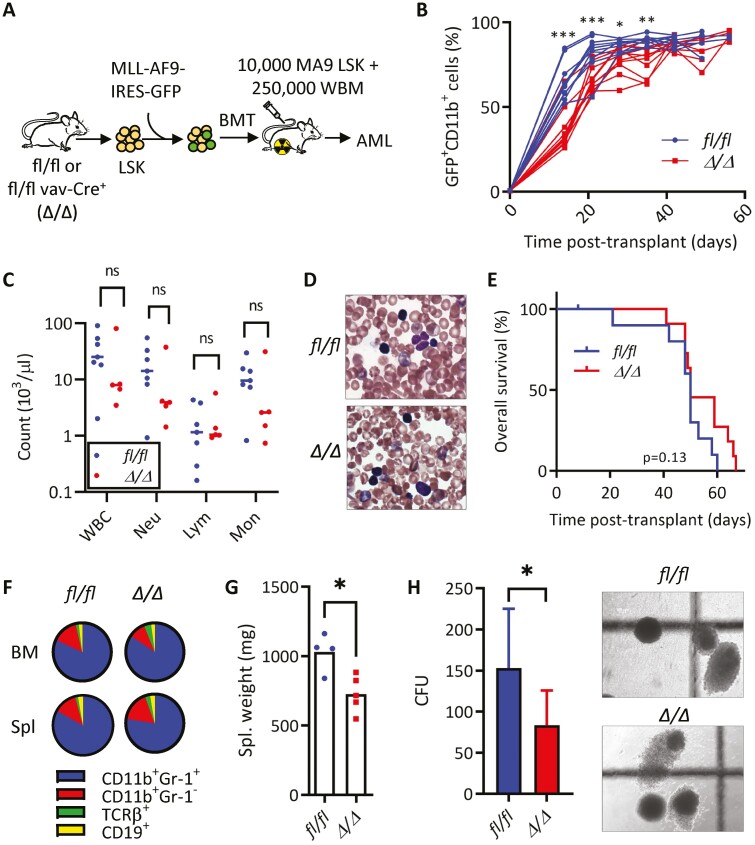
Figure 1.
KLF4 is dispensable for the development of MLL-AF9-induced murine AML but supports disease progression. (A) Schematic diagram of MLL-AF9 (MA9)-induced leukemia using LSK cells from mice with conditional Klf4 deletion. (B) Flow cytometric detection of GFP+ CD11b+ leukemic cells in peripheral blood of fl/fl and Δ/Δ MA9 mice expressed as a percentage of total live cells (n = 10/group). (C) White blood cell counts at 5 weeks post-transplantation. (D) Representative blood smear of fl/fl and Δ/Δ MA9 mice at 7 weeks post-transplantation. (E) Kaplan–Meier analysis of survival of fl/fl and Δ/Δ MA9 mice (n = 10/group). (F) Frequency of myeloid (CD11b, Gr-1) and lymphoid (TCRβ, CD19) cells within GFP+ cells in the bone marrow and the spleen of moribund MA9 mice as determined by flow cytometry. A representative pie chart is shown. (G) Spleen weight of moribund fl/fl and Δ/Δ leukemic mice (n = 4/group). Mean and individual values are shown. (H) Colony-forming cell assay of fl/fl and Δ/Δ MA9 bone marrow cells from moribund mice (n = 7/group). The representative morphology of colonies is shown on the right. The data are represented as mean ± SD and are representative of 3 independent experiments. ns, not statistically significant. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. Two-tailed Student’s t test was used in B, C, G, H. Log-rank test was used in E.