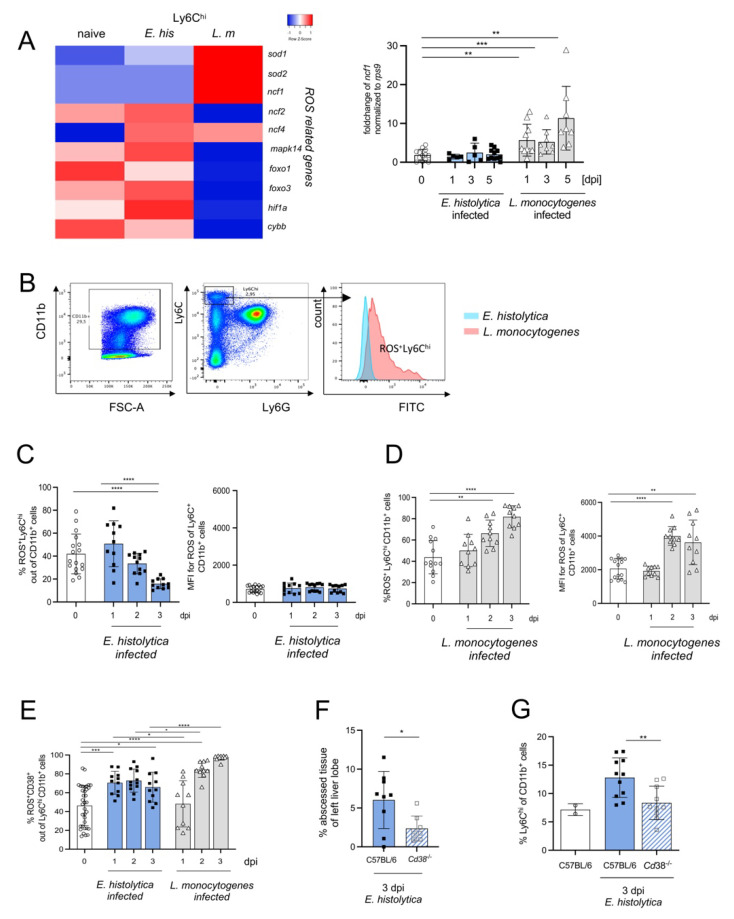
Figure 6.
CD38+Ly6Chi monocytes represent the major monocytic source of ROS production and contribute to liver damage following E. histolytica infection. (A) Heat map of differentially regulated genes involved in ROS production and a graph showing fold changes in expression of Ncf1 mRNA in the liver during infection with E. histolytica or L. monocytogenes. (B) Gating scheme and histogram for ROS+ liver Ly6Chi monocytes. Percentage and mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of ROS+Ly6Chi monocytes during (C) E. histolytica and (D) L. monocytogenes infection. (E) Percentage of ROS+CD38+ out of Ly6ChiCD11b+ monocytes in both infection models. (F) Percentage of amebic liver abscess weight in relation to the left liver lobe in WT (C57BL/6) and Cd38-/- mice. (G) Percentage of Ly6Chi CD11b+ cells in the liver in naive, infected WT and Cd38-/- mice. (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney U test).