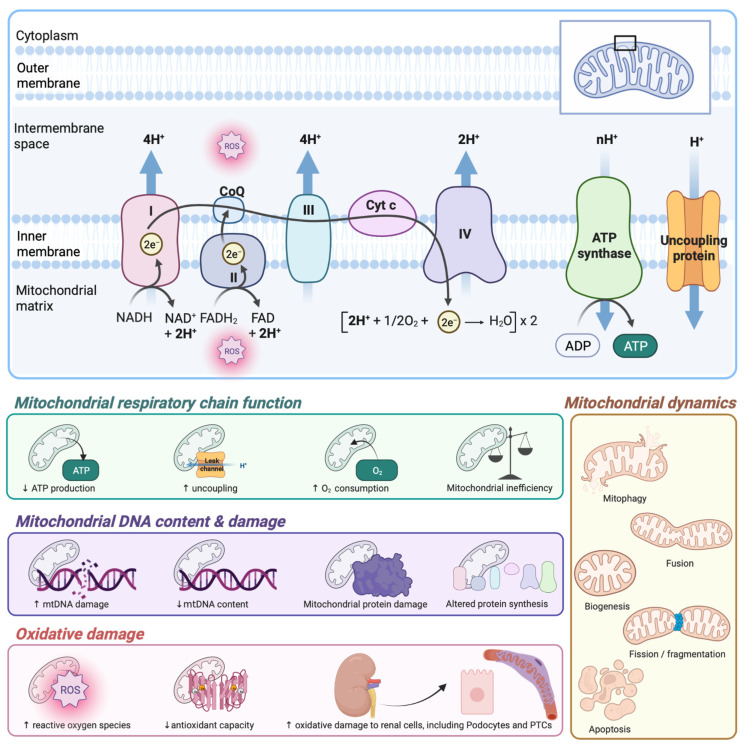
Figure 1.
Potential pathways of mitochondrial dysfunction contributing to and/or exacerbating disturbances in renal oxygenation and energetics in diabetes. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CoQ, coenzyme Q; Cyt C, cytochrome C; e−, electrons; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide (oxidised); FADH2, flavin adenine dinucleotide (hydroquinone); H+, hydrogen ions; H2O, water; mtDNA, mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidised); NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced); O2, oxygen; PTCs, proximal tubule cells; ROS, reactive oxygen species. Image created with BioRender.com.