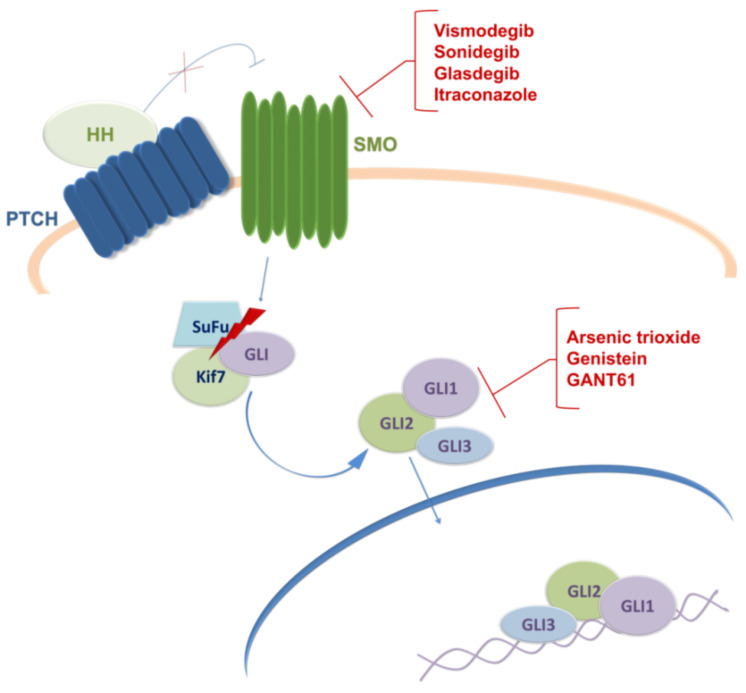
Figure 2.
The canonical activation of HH pathway and its pharmaceutical inhibitors. The activation of pathway occurs when HH ligand binds to PTCH at the cell membrane. In response to this binding, PTCH no longer inhibits SMO and initiates the downstream signaling, causing rapid dissociation of the SuFu–GLI complex and thus allowing GLI to enter the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes. Proven pharmacological inhibitors that target SHH signaling components (SMO receptor or GLI transcription factors) are presented in red. References are included in the main text.