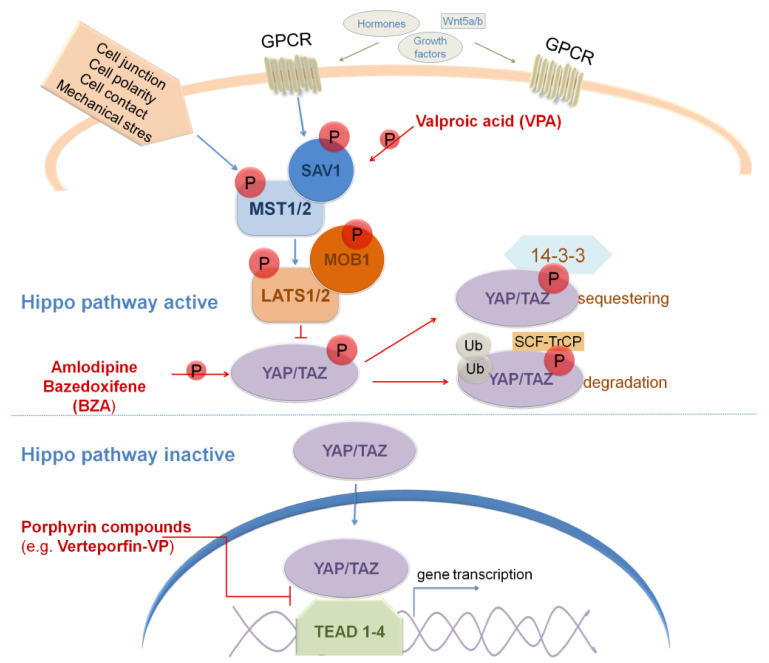
Figure 7.
The canonical Hippo pathway and its pharmaceutical inhibitors. Various extracellular signals including mechanical stress, cellular contact, hormones and growth factors activates Hippo signaling cascades that through serial phosphorylations involving block of kinases inhibits nuclear translocation of transcriptional co-activator YAP/TAZ and consequently their involvement in the regulation of gene transcription. When Hippo pathway is inactive, YAP/TAZ translocates to the nucleus, associates with TEAD family of transcription factors and participates in the regulation of target genes expression. Inhibitors that target important pathway components are indicated in red. References are included in the main text.