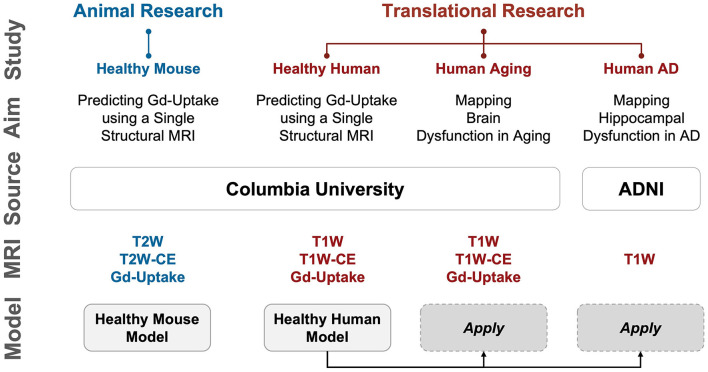
Figure 1.
Overview of the studies conducted. We first performed proof-of-concept studies in mice to validate our hypothesis that deep learning can extract information equivalent to Gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) contrast enhancement from a single-modal non-contrast MRI scan, and then conducted extensive analyses in humans to scrutinize the capability of this proposed approach. Study: A study conducted; Aim: The purpose of the study; Source: where the imaging data come from; MRI: modality/type of data used in the study; Model: specific DeepContrast model used in the study. AD: Alzheimer's disease; ADNI: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative dataset; CBV: cerebral blood volume; Gd-Uptake: GBCA contrast uptake maps; T2W: T2-weighted scans; T2W-CE: T2-weighted contrast-enhanced scans; T1W: T1-weighted scans; T1W-CE: T1-weighted contrast-enhanced scans.