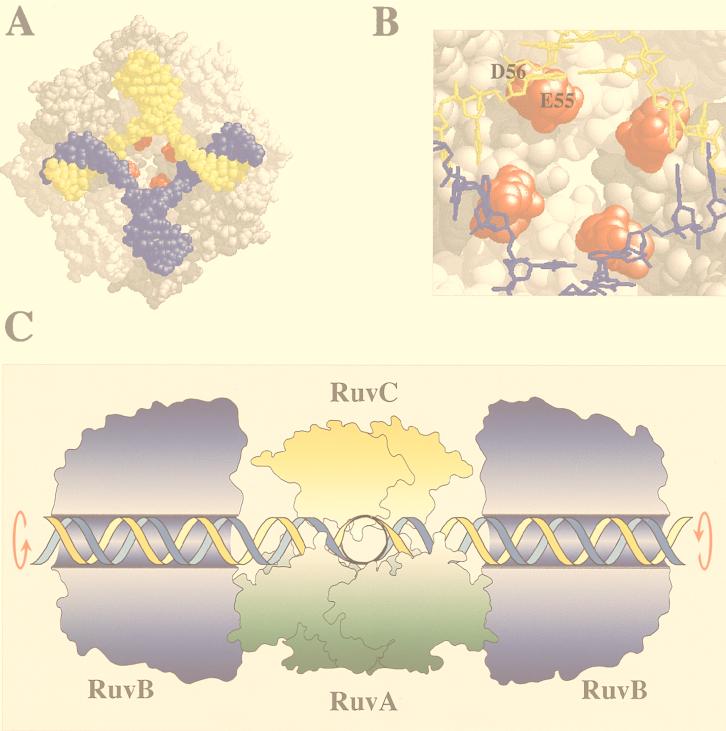
FIG. 2.
Holliday junction processing by RuvABC. (A) Structure of the RuvA tetramer complexed with a Holliday junction (produced with RasMol) (18). The acidic pins are shown in red. (B) Locations of the acidic pin residues (Glu55 and Asp56; colored red) of RuvA, showing their proximity to the phosphate backbone at the junction core. (C) Model of branch migration and resolution by the RuvABC resolvasome. A tetramer of RuvA holds the Holliday junction in a square planar conformation (side view). RuvB hexamer rings encircle duplexes on each side of the RuvA-junction complex. Branch migration is achieved by drawing the duplexes through these rings, generating heteroduplex DNA. A RuvC dimer bound to the upper face of the junction scans for specific target sequences as the DNA passes across RuvA. Symmetrically related incisions are introduced to yield nicked duplexes which can be sealed by DNA ligase. Outlines of RuvA and RuvC were taken from the crystal structures of these proteins (3, 38). The RuvB structure is based on electron micrographs of RuvAB-junction complexes (36). An animated model of branch migration by RuvAB can be viewed at the Krebs Institute web site (23a).