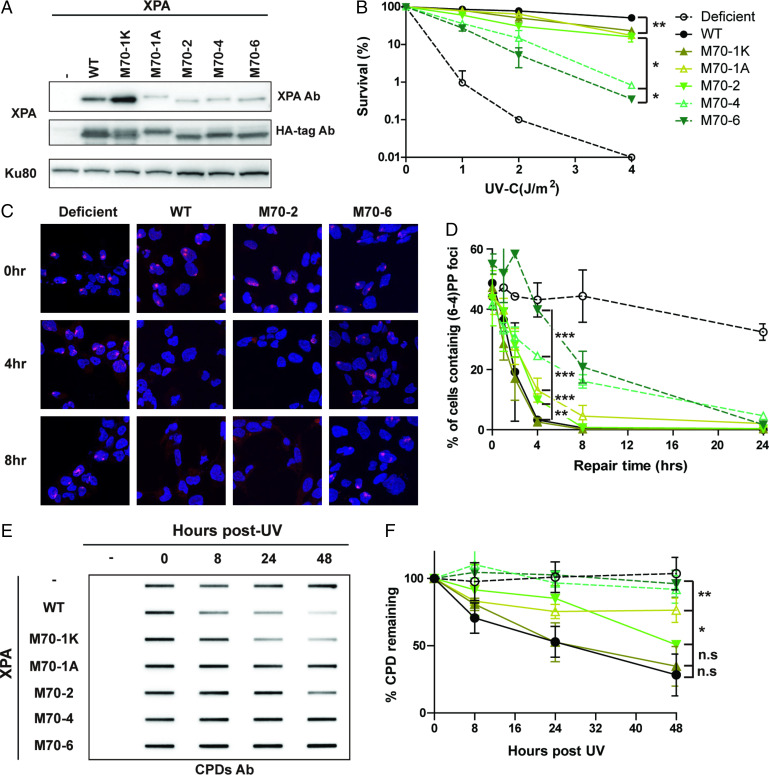
Fig. 2.
Mutations in the RPA70 interaction domain of XPA cause defects in the repair of UV lesions. (A) Expression level of WT and RPA70-interaction mutant XPA in XP2OS cells transduced with HA-tagged XPA. Proteins were detected with anti-XPA and anti-HA antibodies, using Ku80 as a loading control. (B) Clonogenic survival assays. Cells were treated with the indicated UV dose, grown for 10 d and stained with methylene blue. Survival rates were normalized to nontreated cells. The P value was compared to XPA WT. (C) Representative figures of cells irradiated through a 5-µM micropore filter with UV (100 J/m2) and stained with a (6, 4) PP antibody after the indicated times of repair. (6, 4) PP foci are red and cell nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. For microscope analysis, 10X magnification was used with Axio observer 7 (D) Quantification of C: 100 cells were counted for each sample and the data represent at least two independent experiments. The P value was measured compared to XPA WT. (E) Determination of CPD repair kinetics using slot-blot assays. Cells were irradiated with 5 J/m2 genomic DNA isolated at the indicated time points and the levels determined using an anti-CPD antibody CAC-NM-DND-002. (F) Quantification of E, normalized to WT at 0 h. The P value was compared to XPA WT. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.