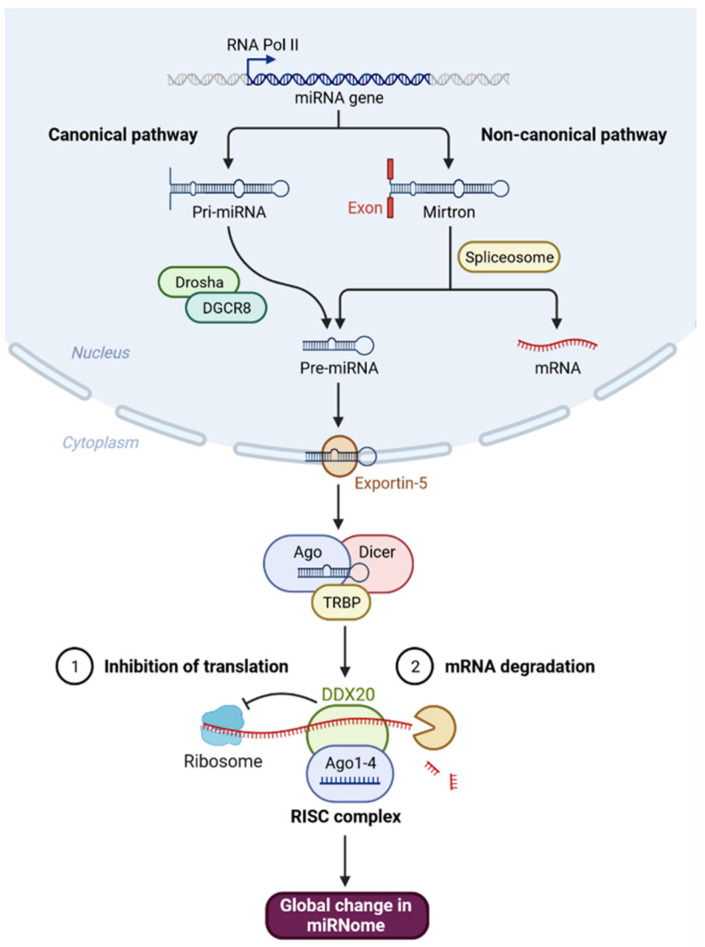
Figure 1.
The role of DDX20 in microRNAs biogenesis through forming RISC complex. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNAs ~22 nucleotides long that bind to target mRNAs, resulting in mRNA degradation or inhibition of mRNA expression. MicroRNAs can be produced from long RNA transcripts. Primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are 1–2 kb long and contain one or more 70-nt hairpin precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs), are excised to pre-miRNAs by DROSHA ribonuclease III (RNase III) and DiGeorge critical region 8 (DGCR8) in the cell nucleus which is exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm by an exportin-5 (XPO5)/Ran–GTP complex. In the cytoplasm, the endoribonuclease Dicer complex catalyzes these pre-RNAs to form miRNAs. The mature miRNAs are loaded into an argonaute 2 (AGO2) protein, which associates with a TAR RNA-binding protein (TRBP), GEMIN4, and DDX20, and forms an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which plays a crucial role in the repression or degradation of mRNAs. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 17 April 2022).