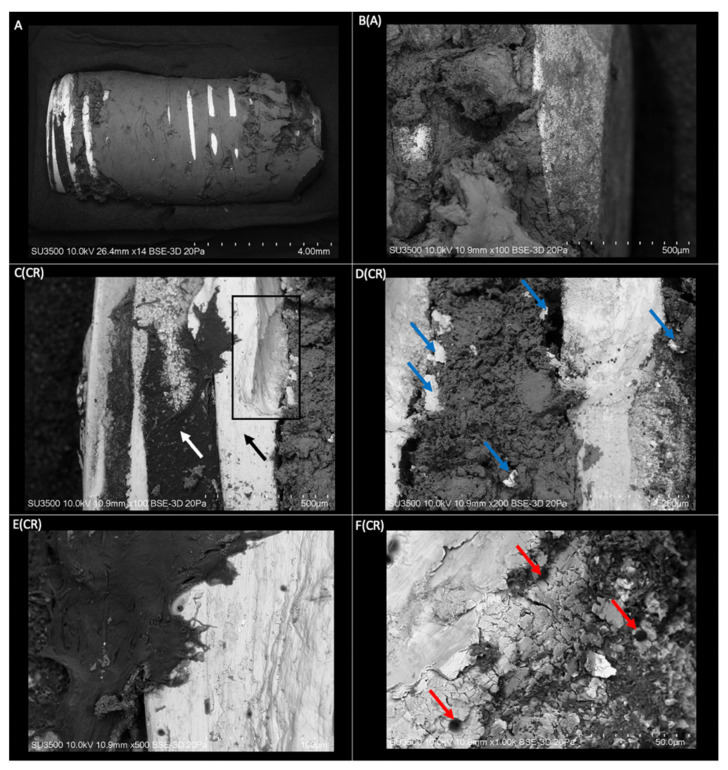
Figure 1.
(A) Three-dimensional structure of a dental implant with mature bone tissue obtained by VP-SEM (Mag: ×14). B(A) Apical view of the implant structure with an integral union of mature bone tissue (Mag: ×100). C(CR) Coronal area of the implant with threads free of bone tissue (black arrow), and depth of the threads with the presence of organic tissue (white arrow). Area of the implant threads with a defect in its structure (rectangle) (Mag: ×100). D(CR) Coronal view of the implant with an integral union of bone tissue between the threads. Spalling of the implant surface lodged in the bone tissue (blue arrows) (Mag: ×200). E(CR) Coronal area thread of the implant with a higher magnification. A rough structure with linear irregularities is displayed in orientation to the implant threads (Mag: ×500). F(CR) View of a thread with higher magnification. Visualization of roughness on the implant surface. Presence of bone tissue penetrates the roughness and blood cells on the surface of the implant (red arrows) (Mag: ×1000).