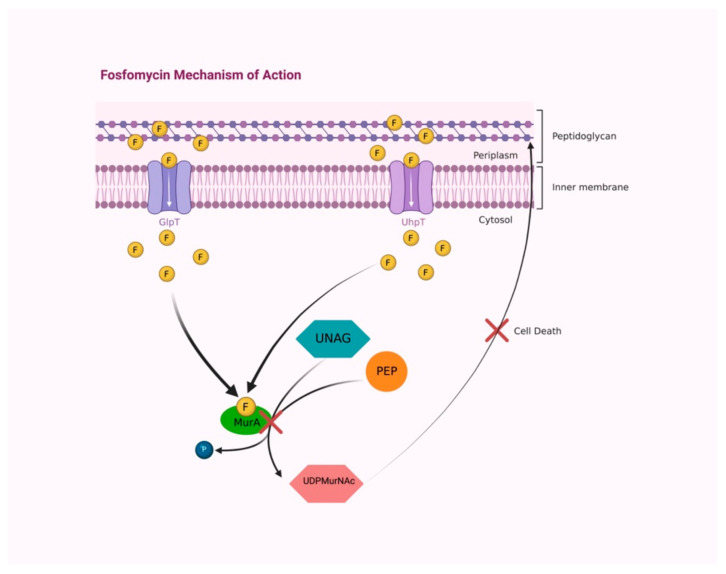
Figure 2.
Fosfomycin accesses into the bacterial wall by two transport uptake systems, GlpT and UhpT. In the cytoplasm, fosfomycin covalently binds to the active site of MurA enzyme, preventing the reaction between PEP and UNAG and avoiding UDPMurNAc synthesis, resulting in peptidoglycan building interruption and causing bacterial-cell death. Abbreviations: F, fosfomycin; GlpT, L-alpha- glycerophosphate transport system; UhpT, hexose-6-phosphate transport system; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; UNAG, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine; MurA, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase; P, phosphate; UDPMurNAc, UDP N-acetylmuramic acid. Created with BioRender.com; accessed on 3 August 2022.