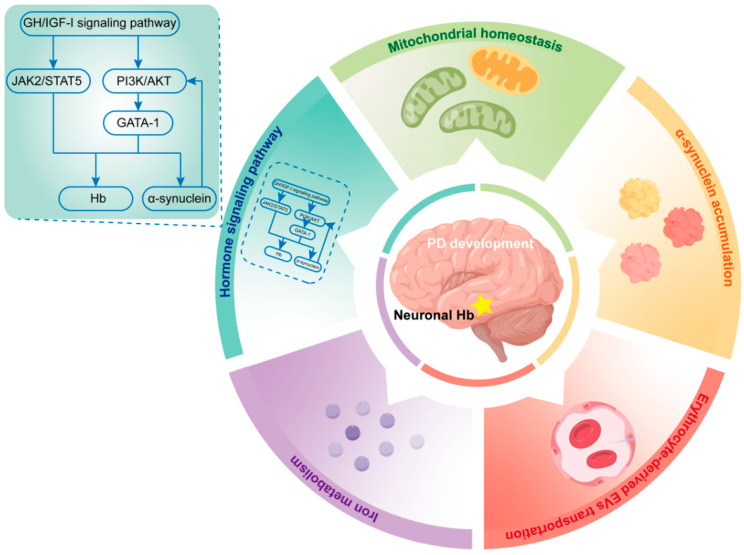
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms through which hemoglobin is involved in PD development. Several potential mechanisms were associated with the roles of hemoglobin to PD development. These mechanisms were established to be involved mitochondrial homeostasis, α-synuclein accumulation, iron metabolism, hormone regulation, and erythrocyte-derived EVs transportation. Hb, hemoglobin; PD, Parkinson’s disease; GH, Growth hormone; IGF-I, insulin-like growth factor-I; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; GATA-1, GATA-binding factor 1.