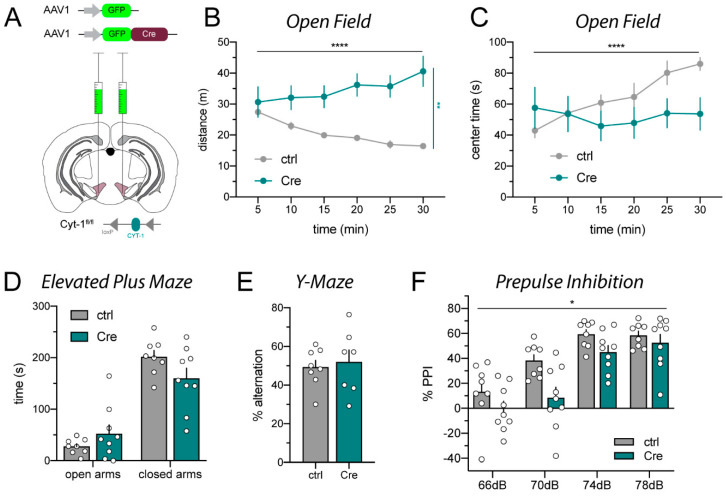
Figure 1.
AAV1_Cre-GFP injections into the VTA of ErbB4 Cyt-1fl/fl mice cause hyperactivity and sensorimotor gating deficits relative to AAV1_GFP injected ErbB4 Cyt-1fl/fl controls. (A) Scheme visualizing bilateral injection of Cre (AAV1_Cre-GFP) and control (AAV1_GFP; both 1013 GC/mL; for details see Figure S1) into the VTA of adult ErbB4 Cyt-1fl/fl mice. (B,C) Locomotor activity in a novel environment was analyzed in the open field (ctrl n = 8, Cre n = 9). Cre-injected mice became hyperactive compared to control-injected mice ((B), two-way ANOVA, F(5,75) = 6.871, p < 0.0001 ****; genotype: p = 0.0013 **) and tend to spend less time in the center over time ((C), two-way ANOVA, F(5,75) = 7.106, p < 0.0001 ****; genotype: p = 0.2769). (D) Anxiety assessed in the elevated plus maze is unchanged (two-way ANOVA, F(1,15) = 2.848, p = 0.1122; genotype: p = 0.3752; ctrl n = 8, Cre n = 9). (E) Spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze is unaltered (unpaired t test, p = 0.7095; ctrl n = 8, Cre n = 7). (F) Prepulse inhibition is impaired in Cre-injected mice compared to controls (two-way ANOVA, F(3,45) = 2.237, genotype: p = 0.0334 *; ctrl n = 8, Cre n = 9).