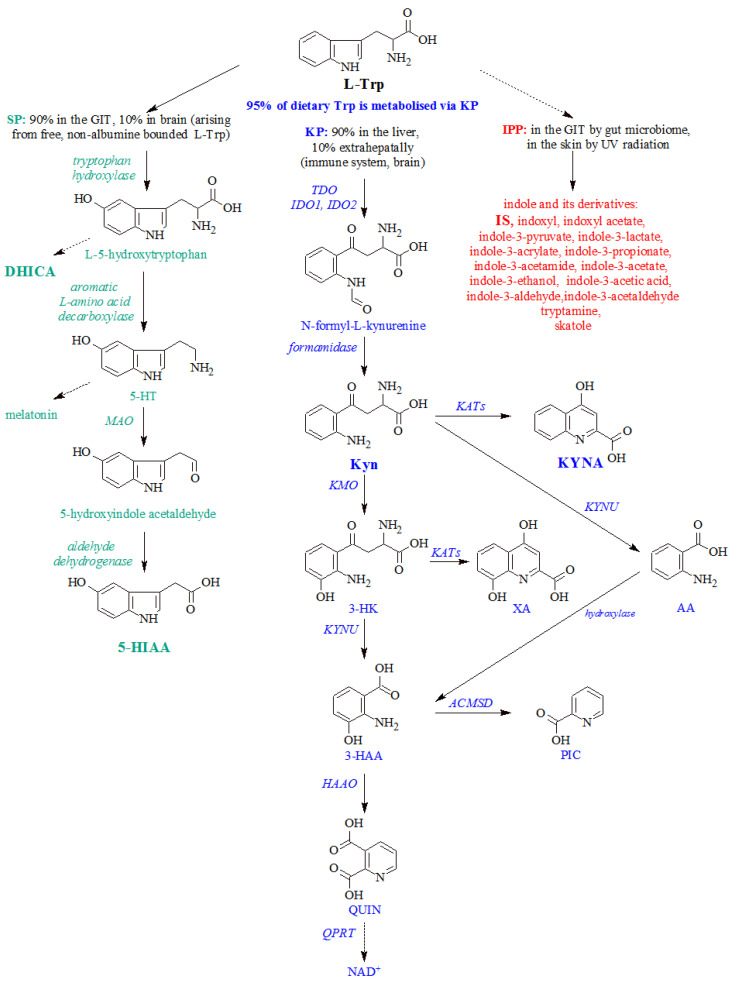
Figure 1.
The three pathways of tryptophan metabolization are the kynurenine pathway, serotonin pathway, and the indole pathway. KP—kynurenine pathway, SP—serotonin pathway, IPP—indole pyruvate pathway; L-Trp—L-tryptophan, Kyn—kynurenine, 3-HK—3-hydroxykynurenine, 3-HAA—3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, QUIN—quinolinic acid, NAD+—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, KYNA—kynurenic acid, AA—anthranilic acid, XA—xanthurenic acid, PIC—picolinic acid, 5-HT—serotonin, 5-HIAA—5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid, DHICA—5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid, IS—indoxyl sulfate; TDO—tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase, IDO1—indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1, IDO2—indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2, KMO—kynurenine 3-monooxygenase, KYNU—kynureninase, HAAO—3-hydroxyanthranilic acid oxygenase, QPRT—quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase, KATs—kynurenine aminotransferases, ACMSD—2-amino-3-carboxymuconate-6-semialdehyde decarboxylase, MAO—monoaminooxygenase; dashed arrows include more catalytic reaction steps; metabolites analyzed in this study are highlighted in bold.