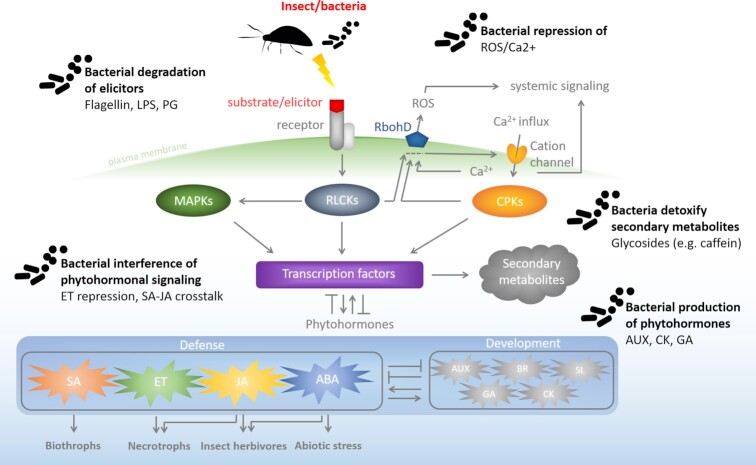
Figure 1.
Overview of insect-associated microbe interference with plant defense signaling. Plant stress perception leads to the activation of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases (RLCKs), mitogen activated kinases (MAPKs), and Ca2+ influx, which in turn results in the activation of calcium-dependent protein kinases (CPKs). Ca2+, RLCKs, and CPKs are involved in the activation of RbohD, which produces extracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) that together with Ca2+ acts as second messenger in systemic signaling throughout the plant. Activation of CPKs, RLCKs, and MAPKs leads to downstream stress signaling, involving the activation of transcription factors that regulate the production of phytohormones and secondary metabolites. Crosstalk between (phytohormonal) signaling pathways is further explained in the main text. ABA, abscisic acid; AUX, auxin; BR, brassinosteroids; CK, cytokinins; ET, ethylene; GA, gibberellin; JA, jasmonic acid; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; PG, peptidoglycan; SA, salicylic acid; and SL, strigolactones.