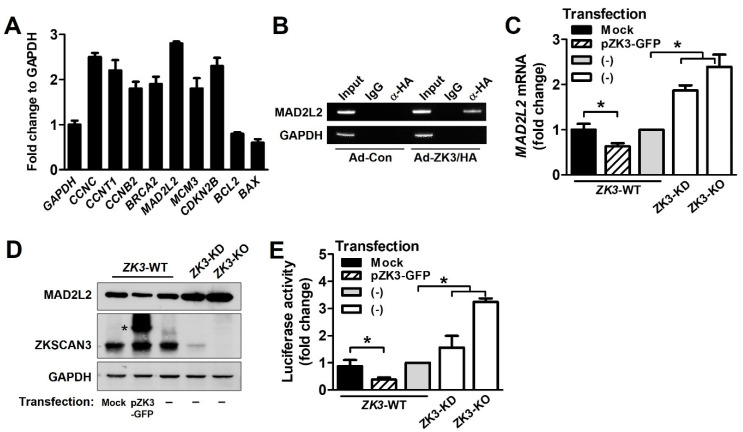
Figure 5.
ZKSCAN3 acts as a transcriptional repressor of MAD2L2. (A) Chip assay and qPCR array were performed using EpiTect® ChIP qPCR array Human Cell Cycle (QIAGEN). HCT116 cells were transduced with Ad-ZK3/HA or Ad-Con for 24 h and the crosslinked lysates were sonicated. The sonicated lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody or IgG and then with protein A. The eluted precipitates were applied to a qPCR array (QIAGEN). Representative qPCR results from the array are presented. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of triplicate experiments; GAPDH expression was used as the internal control. (B) Cells were infected with Ad-Con or Ad-ZK3/HA for 24 h, treated with formaldehyde, and sonicated. The cross-linked DNA–protein complex was immunoprecipitated using anti-HA (α-HA) antibody or IgG followed by PCR amplification for MAD2L2 promoter. Immunoprecipitates obtained using IgG were used as the negative controls. Input chromatin (Input) refers to sonicated chromatin before immunoprecipitation. (C) Real-time qPCR was performed to evaluate the expression of MAD2L2 using mRNA extracted from the indicated cells. Data obtained from three independent experiments were used to represent a fold increase in mRNA levels. Statistical significance was determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test (* p < 0.05). (D) Western blotting was performed to evaluate the expression of MAD2L2 and ZKSCAN3 proteins; GAPDH was used as the loading control. *, ectopic ZKSCAN3 (E) The indicated cells were transfected with pGL-MAD2L2. The luciferase activity was determined. Data are expressed as fold change in expression compared to that in control cells, from three independent experiments; they are expressed mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test. (* p < 0.01).