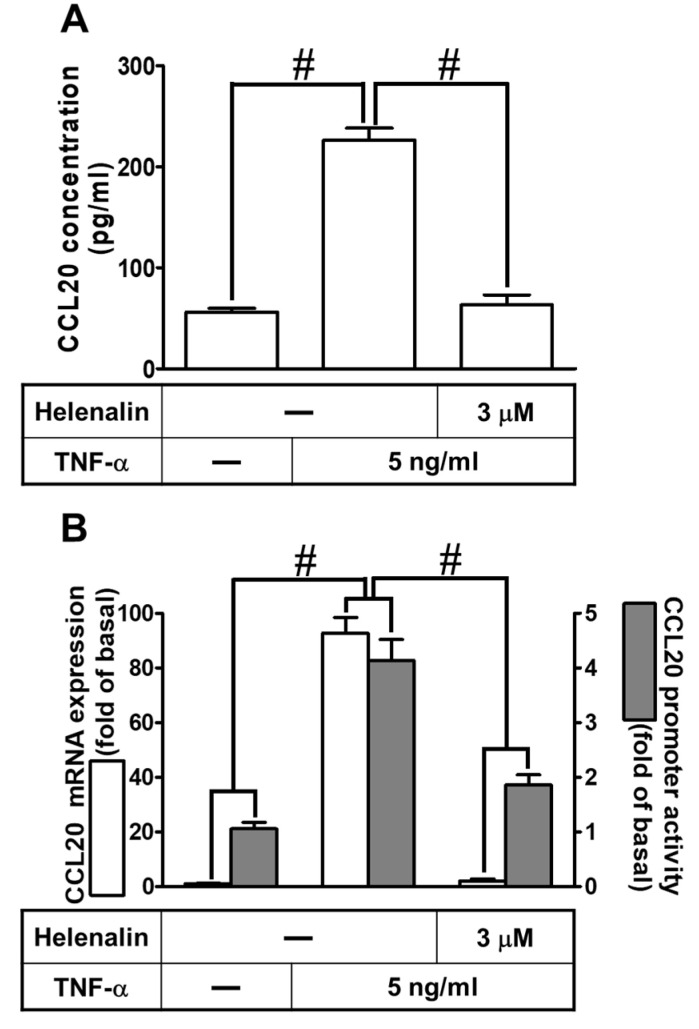
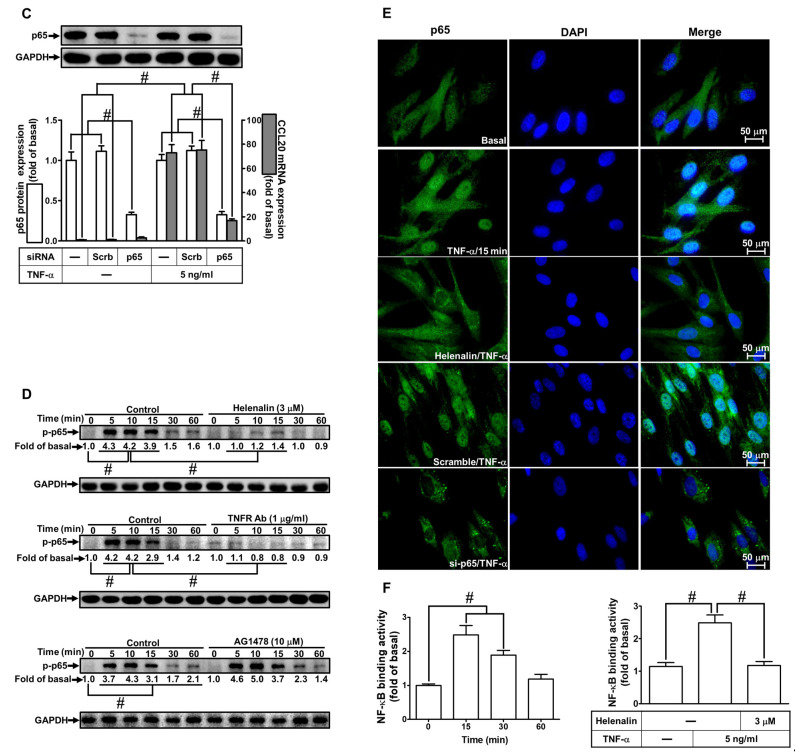
Figure 7.
Involvement of NF-κB p65 in TNF-α-induced CCL20 expression. (A) Cells were pretreated with 3 μM helenalin for 1 h and then incubated with 5 ng/mL TNF-α for 12 h. The conditioned media were utilized to determine the CCL20 level via an ELISA kit. (B) Cells were pretreated with 3 μM helenalin for 1 h and then incubated with 5 ng/mL TNF-α for indicated time intervals. The mRNA levels and promoter activity of CCL20 were determined by real-time PCR (2 h) and promoter assay (4 h), respectively. (C) Cells were transfected with scrambled or p65 siRNA and then incubated with TNF-α for 2 h. The mRNA levels of CCL20 were determined by real-time PCR. The protein levels of p65 were determined by Western blot with GAPDH as a loading control. (D) Cells were pretreated without or with 3 μM helenalin, 1 μg/mL TNFR1 Ab, or 10 μM AG1478 for 1 h and then treated with TNF-α for the indicated times (0, 5, 10, 15, 30, and 60 min). The phosphorylation of p65 was determined by Western blot with GAPDH as a loading control. (E) Cells were pretreated without or with helenalin (3 μM) for 1 h or transfected with scrambled or p65 siRNA, and then incubated with TNF-α for 15 min. Cells were fixed and then labeled with an anti-phospho-p65 antibody and then a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. The localization and expression of phospho-p65 were determined by immunofluorescent staining (green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 50 µm. (F) Cells were pretreated without or with 3 μM helenalin for 1 h and then stimulated with TNF-α for the indicated time intervals or 15 min. The binding of NF-κB p65 to the promoter region of CCL20 was determined with a ChIP assay. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments (n = 3). # p < 0.05, as compared with the cells exposed to vehicle alone; or significantly different as indicated.