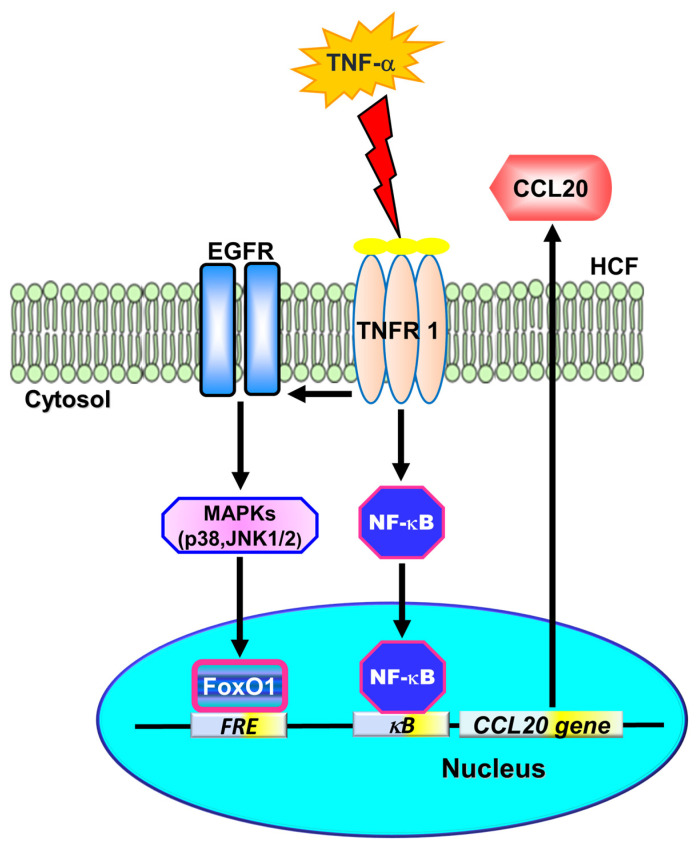
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram illustrating the proposed signaling pathway involved in TNF-α-induced CCL20 expression and secretion in HCFs. TNF-α-induced CCL20 expression was, at least partially, mediated through binding to TNFR1 leading to transactivation of EGFR. Activated EGFR promoted the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK- or JNK1/2-dependent FoxO1 activation, which further bound with the FoxO1 response element (FRE) on the CCL20 promoter. In addition, TNF-α also turned on NF-κB transcription factors. Either FoxO1 or NF-κB activation could enhance the expression of CCL20 induced by TNF-α, which may be engaged in the inflammatory responses in HCFs. A better understanding of mechanisms underlying the regulation of the CCL20 gene by TNF-α will support more opportunities to develop anti-inflammatory therapeutic strategies for treating cardiac inflammation.