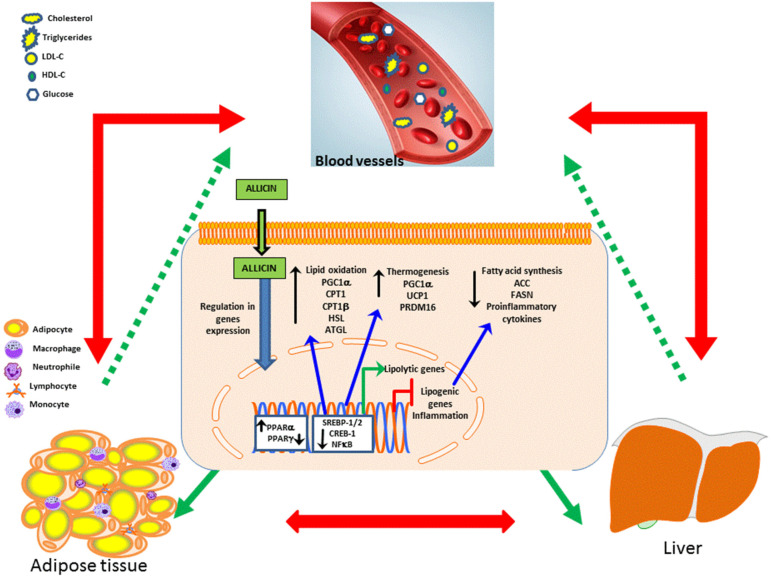
Figure 3.
Effects of allicin on lipid metabolism: Allicin crosses the cell membrane and modulates transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes associated with lipid oxidation, thermogenesis, fatty acid synthesis and proinflammatory cytokines in the liver and adipose tissue improving the lipid profile. The red arrows indicate the close association between liver and adipose tissue dysfunction and its influence on the serum levels of the lipid profile and glycemia. The green arrows indicate the beneficial effects of allicin at the intracellular level in adipose and liver tissue and the final effect at the systemic level. Abbreviations: acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FASN), AMP response element-binding protein (CREB); Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) and SREBP-2; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα); PPAR gamma (PPARγ); Pparγ coactivator 1α (Pgc1α); hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL); Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL); Uncoupling protein-1 (Ucp1); PR-domain containing 16 protein (Prdm16); low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C); high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C).