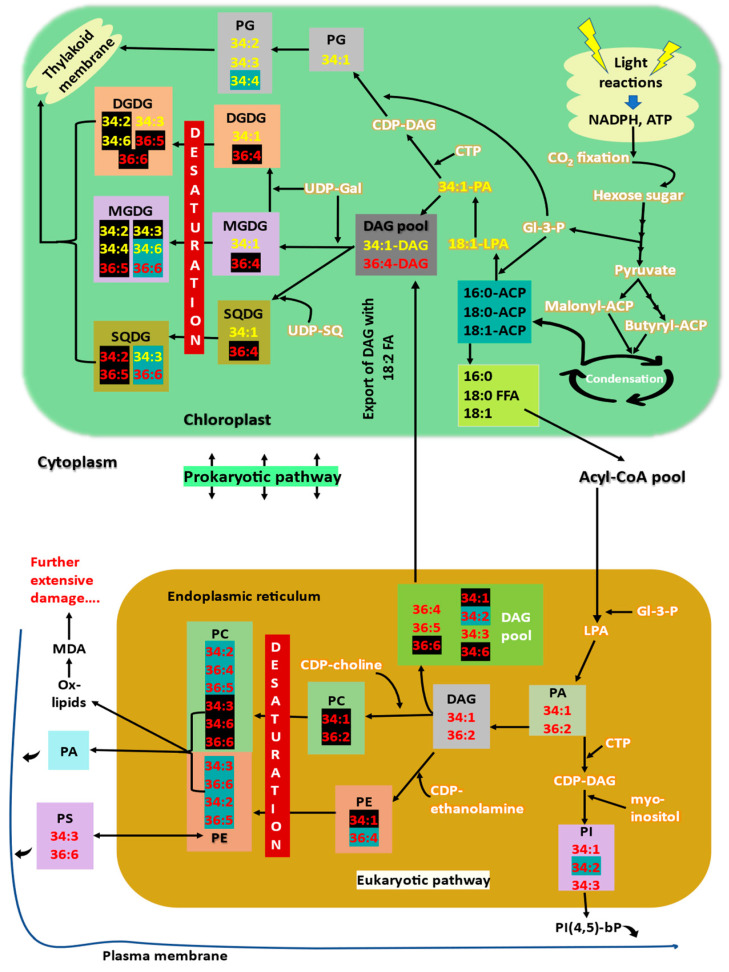
Figure 1.
Overview of the fatty acid de novo and lipid biosynthetic pathways (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) in chloroplast and endoplasmic reticulum with major lipid remodelling changes occurring in the pathways under high-temperature conditions. Prokaryotic pathway lipids are represented in yellow and eukaryotic lipids are represented in red. Lipids highlighted in blue are decreased, and those highlighted in black increase under high temperatures. The figure showing the steps of fatty acid and lipid biosynthesis is modified from Holzl and Dormann [46] and Higashi and Saito [63]. Collectively, the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis yield pyruvate. The pyruvate dehydrogenase in chloroplast links the pyruvate metabolism and de novo fatty acid biosynthesis yielding the acetyl-CoA. Several condensation steps occur to provide 16:0-ACP, 18:0-ACP, and 18:1-ACP for prokaryotic lipid synthesis pathway or exported into ER for utilisation in eukaryotic lipid synthesis pathway. The fatty acids exported to ER are then made into DAGs and exported back to chloroplast for plastidic lipid synthesis. Under high temperatures, overall contribution of prokaryotic pathway for galactolipid synthesis is reduced, and eukaryotic pathway is increased. Abbreviations: FFA, free fatty acid;16:0, palmitic acid; 16:3, hexadecatrienoic acid; 18:0, stearic acid; 18:1, oleic acid; 18:2, linoleic acid; 18:3, linolenic acid; ACP, acyl carrier protein; Gro-3-P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; CDP, cytidine diphosphate; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; UDP, uridine diphosphate; DAG, diacyl glycerol; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid, PA, phosphatidic acid; PG, phosphatidyl glycerol; PC, phosphatidyl choline; PE, phosphatidyl ethanolamine; PS, phosphatidyl serine; PI, phosphatidyl inositol; PI(4,5)-bP, phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-bisphosphate; MGDG, monogalactosyl diacylglycerol; DGDG, digalactosyl diacylglycerol; SQDG, sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol; MDA, malondialdehyde.