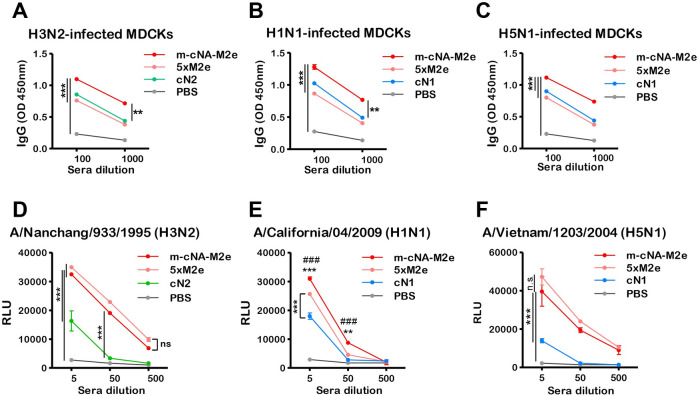
Fig 7. IgG antibodies recognizing cell surface viral antigens and ADCC functional activities by m-cNA-M2e VLP-vaccination.
(A-C) IgG antibodies recognizing cell surface viral antigens. MDCKs were infected with influenza A viruses (A/Nanchang/933/1995 H3N2, A/California/04/2009 H1N1, and rgA/Vietnam/1203/2004 H5N1). The levels of IgG binding to virus antigens expressed on MDCKs were determined by ELISA. Binding reactivity of immune sera to H3N2- (A), H1N1- (B), H5N1- (C) infected MDCKs. (D-F) ADCC reporter assays of antisera from immunized mice, against MDCK target cells infected with A/Nanchang/933/1995 (H3N2) (D), A/California/04/2009 (H1N1) (E), and rgA/VN/1203/2004 H5N1 (F). Subsequently, the ADCC reporter assay was performed using Jurkat effector cells expressing mouse FcrRIII, and the relative luminescence unit (RLU) was measured. The statistical significances were performed with two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest and indicated as **, P < 0.01; ***,###, P < 0.001 (compared among the m-cNA-M2e and PBS or monomeric cN control groups); ns, no significant difference between two compared groups.