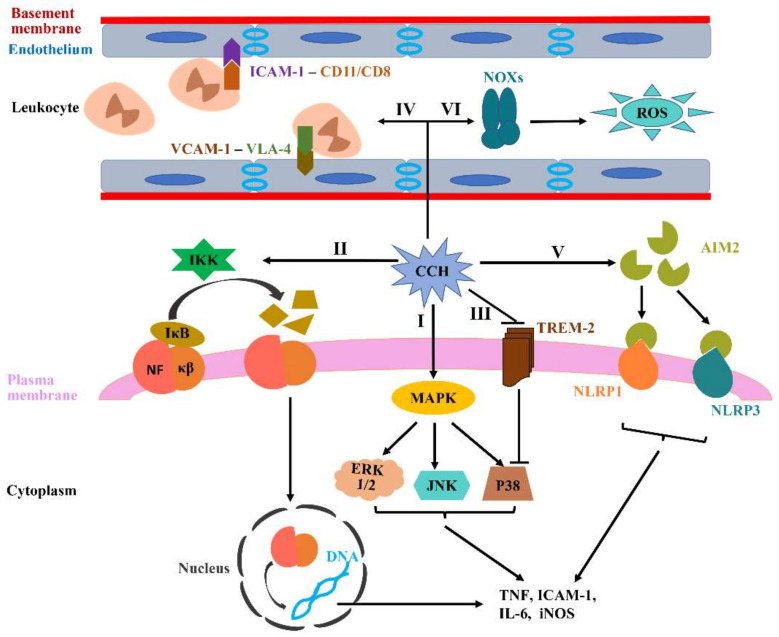
Figure 2.
CCH-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. (I–III) The activated microglia by CCH can generate various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF, in which multiple signaling pathways are involved, including MAPKs, NF-κβ and TREM-2. (IV) CCH can directly accelerate endothelium activation. Activated endothelium express more ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 to bind to CD11/CD18 and VLA-4, which contribute to the adherence and extravasation of leukocytes into brain parenchyma. (V) AIM2 inflammasome signaling can be activated during CCH, which increases microglial activation and subsequently promotes the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. (VI) NOXs, recognized as the primary source of ROS in the brain, are thought to be the key contributing factors to CCH-related oxidative stress.