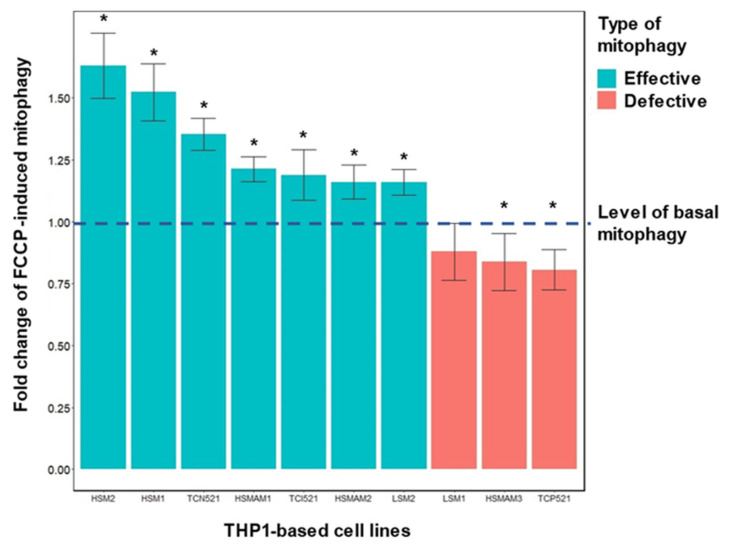
Figure 7.
Induction of mitophagy with FCCP in cybrid lines carrying atherosclerosis-associated mtDNA mutations. Shown is the change in mitophagy under the influence of FCCP relative to the basal level of mitophagy in ten cybrid lines. Mitophagy was assessed as a 12 h colocalization of mitochondria and lysosomes, which were labeled with MitoTracker Green FM (200 nM) and LysoTracker Red DND-99 (50 nM), respectively. FCCP (2 μM) was used for stimulation of colocalization in the experiments with induced mitophagy. Confocal images were obtained using a Zeiss 900 confocal microscope equipped with a 63× oil immersion objective. MitoTracker Green fluorescence intensity was obtained with 488 nm excitation and 500–530 nm emission filter. The 561 nm excitation line and 566–700 nm emission filter were used for LysoTracker Red DND-99. Colocalization was calculated with ZEISS ZEN 3.1 (blue edition) software as the relative number of colocalized pixels in MitoTracker Green in relation to the total number of pixels above the threshold value. The basal level of mitophagy was taken as one and marked with a dotted line. Cybrid lines with efficient mitophagy, i.e., with increased intensity of mitophagy under the influence of FCCP, are represented in green. Cybrid lines with defective mitophagy, i.e., either not different from the basal level or below the basal level, are marked in red. An asterisk indicates significant differences between induced mitophagy and basal mitophagy, p < 0.05, according to the results of the Wilcoxon non-parametric paired test [31].