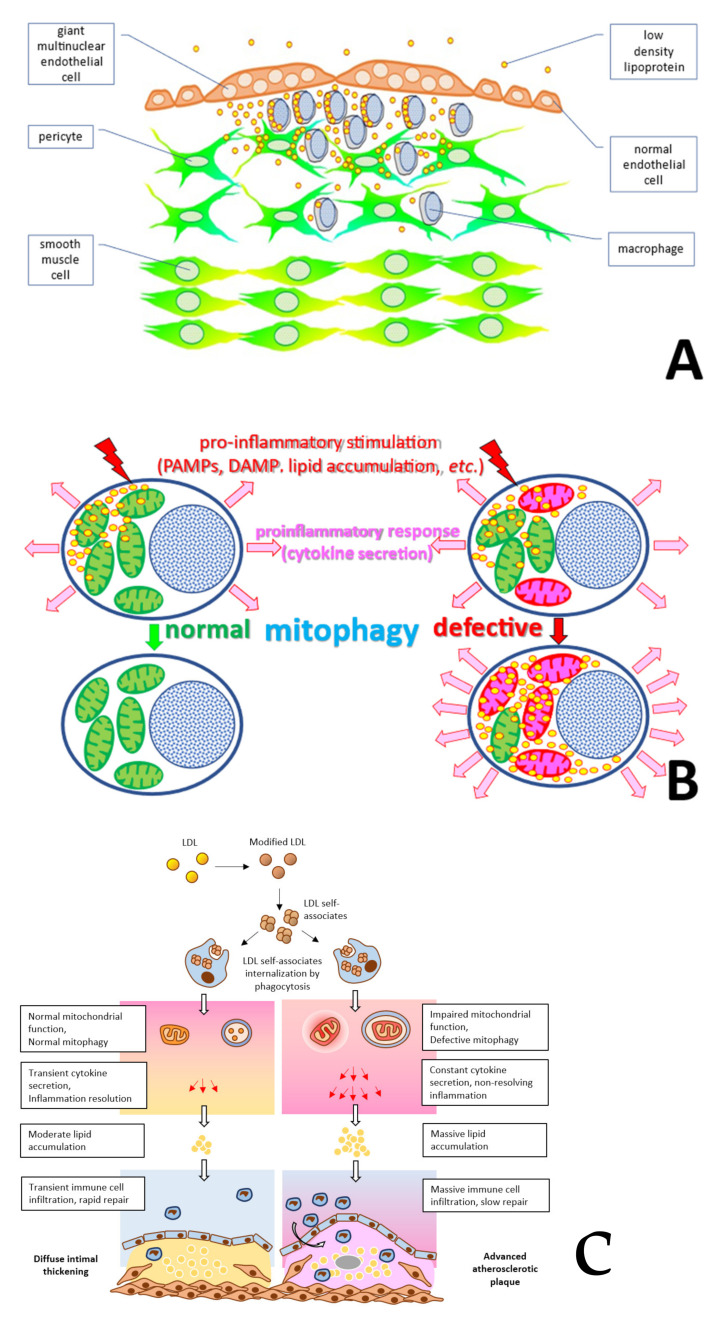
Figure 10.
Proposed mechanisms of chronic inflammation in atherogenesis. (A) Accumulation of circulating immune cells and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) taking place preferentially in the areas enriched with giant multinucleated endothelial cells. (B) Pro-inflammatory signaling initiated in response to uptake of modified LDL can become persistent in presence of defective mitophagy. (C) Normal resolution (left) and chronification of inflammation (right) in the arterial wall lead alternatively either to diffuse thickening or to persistent inflammation and atherosclerotic plaque formation. (Panel C reprinted with permission from [27], 2020, MDPI).