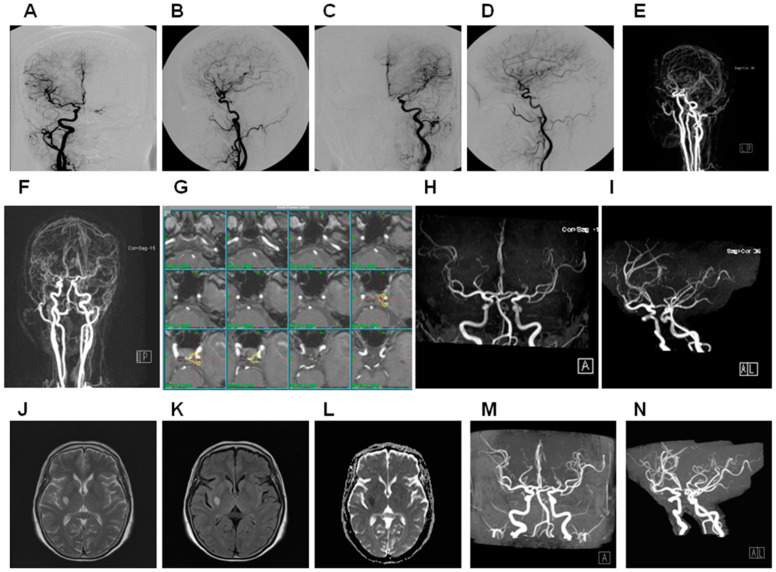
Figure 3.
Illustration of right carotid cavernous sinus fistula treated by GKRS with late onset of brain infarct. A 52-year-old female suffered left abducense nerve palsy for 5 months and received GKRS targeted on left cavernous sinus. The total obliteration of the fistula and recovery of nerve function was noted. However, she suffered right-side putamen infarct, which was not related to irradiation to the right internal carotid artery. (A) Cerebral angiography in PA view in right CCA injection. (B) Cerebral angiography in lateral view in right CCA injection. (C) Cerebral angiography in PA view in left CCA injection. (D) Cerebral angiography in lateral view in left CCA injection. (E) Cerebral MAR lateral view. (F) Cerebral MRA in PA view. (G) Demonstration of GKRS with treated volume of 0.21 cc in 20 Gy (50% line), yellow line: 50% line. (H) Cerebral MRA in PA view 2 years after GKRS. (I) Cerebral MRA in lateral view 2 years after GKRS. (J) MRA in T2 weight showed a hypersignal lesion over right putamen 13 years after GKRS. (K) MRA in FLAIR showed a hypersignal lesion over right putamen 13 years after GKRS. (L) MRA in DWI showed a hypo-signal lesion over right putamen 13 years after GKRS. (M) MRA in PA view showed no definite carotid stenosis 13 years after GKRS. (N) MRA in lateral view showed no definite carotid stenosis 13 years after GKRS. ECA, ICA, and MRA: see text. CCA: common carotid artery; FLAIR: fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; DWI: diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.