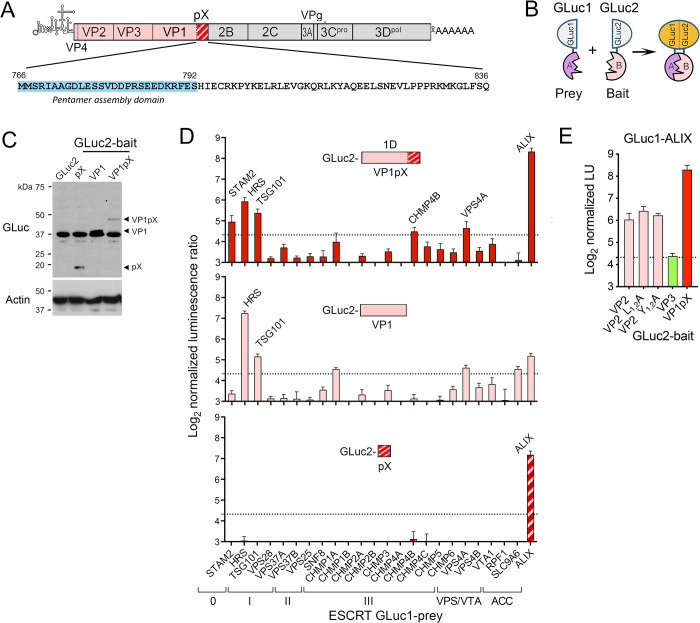
Fig 1. Protein fragment complementation screen for VP1pX interactions with ESCRT.
(A) HAV genome organization: capsid proteins are in color with pX hatched. Below is the pX sequence of p16 virus. (B) Protein-fragment complementation assay with ‘bait’ and ‘prey’ proteins fused to N-terminal GLuc1 and C-terminal GLuc2 Gaussia princeps luciferase fragments [26]. (C) Representative GLuc immunoblot showing expression levels of GLuc2 bait proteins fused to VP1pX (1D), VP1, or pX in 293T cells. Actin included as a loading control. (D) Screen for interactions of (top) VP1pX, (middle) VP1, and (bottom) pX with ESCRT components. Normalized light units (LU) >20 (dashed line) exceed values from a large panel of control prey proteins [27]. Acc: ESCRT accessory protein. (E) Results of protein-fragment complementation assay assessing interactions of GLuc1-ALIX prey with VP2, VP2 late domain mutants with Ala substitutions of Leu (L1-2A) and Tyr residues (Y1-2A) (14), VP3, or VP1pX fused to GLuc2 as bait. Data in C and E are means from 2 independent experiments, each with 3 technical replicates.