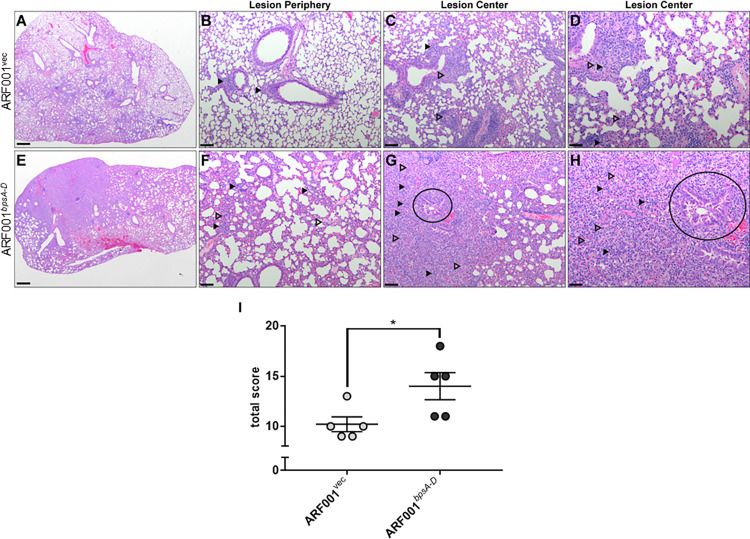
Fig 7. Bps converts E. coli to a respiratory pathogen in C57BL/6 mice.
Pulmonary infection with E. coli expressing bpsA-D results in severe pneumonia (e-h) compared to E. coli expressing the empty vector (a-d). ARF001bpsA-D-infected mice: Neutrophils (filled arrows) admixed with edema (open arrows) at lesion periphery (f) and large numbers of neutrophils (filled arrows), macrophages (open arrows) with bronchiolar epithelial hyperplasia, dysplasia and necrosis (circle) at lesion center (g, h). ARF001vec-infected mice: few mixed leukocytes (arrows) at lesion periphery (b) and multifocal, small numbers of neutrophils (closed arrow) and moderate numbers of macrophages (open arrow) around bronchioles (c, d). Scale bar in a, e = 500 μm, 20x total magnification; Scale bar in b, c, f, g = 100 μm, 100x total magnification; Scale bar in d, h = 50 μm, 200x total magnification.