Figure 6.
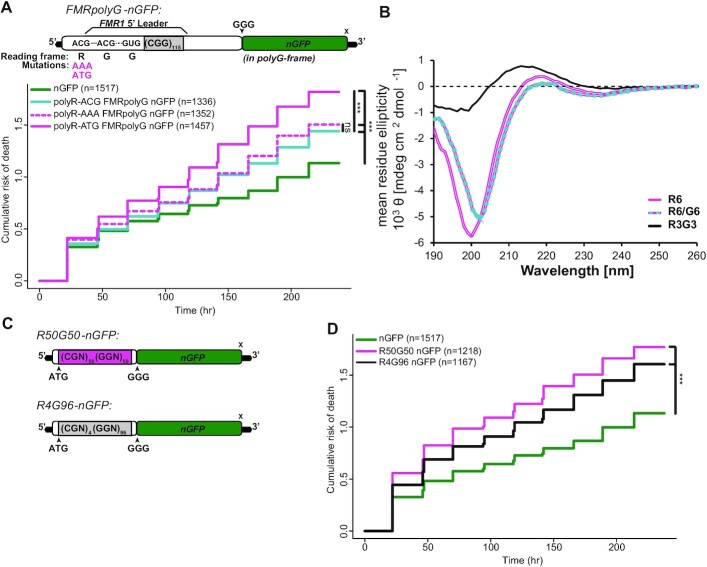
Chimeric peptides exhibit unique biophysical properties and induce neurotoxicity. (A) Top: schematic of FMRpolyG-nGFP reporter with CGG115, and polyR-frame ACG mutated to AAA to preclude translation initiation and to ATG to promote translation initiation. Bottom: survival analysis by longitudinal fluorescence microscopy on primary rat cortical neurons expressing FMRpolyG with native polyR-ACG (blue), or with ACG mutated to AAA (dotted pink) or ATG (pink) (relative to nGFP (green); polyR-ACG: P< 4.82e-06; polyR-AAA: P = 7.73e−09, polyR-ATG: P< 2e−16) (polyR-ACG v polyR-AAA: P = 0.235; polyR-ACG versus polyR-ATG: P = 9.42e−08). (B) CD measurements show that the spectra of R6 (0.3mg/mL, pink) and R6/G6 mixtures (0.3 mg/mL of each peptide, pink/blue dashed line) differ, suggesting that the secondary structure of R6 is altered in the presence of G6. The spectra of chimeric R3G3 (0.3 mg/ml, black) is also distinct than R6 and R6/G6 mixture. Spectra of G6 is not shown because glycine is achiral and does not produce CD signal. (C) Schematic of polymer expression vectors with optimized alternative codon sequences to express 50 arginines followed immediately by 50 glycines (R50G50), and four arginines followed by 96 glycines (R4G96) upstream of GFP. (D) Survival analysis by longitudinal fluorescence microscopy on primary rat cortical neurons expressing polymers R50G50 (pink) or R4G94 (black) (relative to nGFP (green): R50G50: P< 2e−16, R4G96: P = 4.36e−15). (A, D) n, number of neurons; Cox proportional hazard analysis. n.s. = not significant, ***P< 0.001.