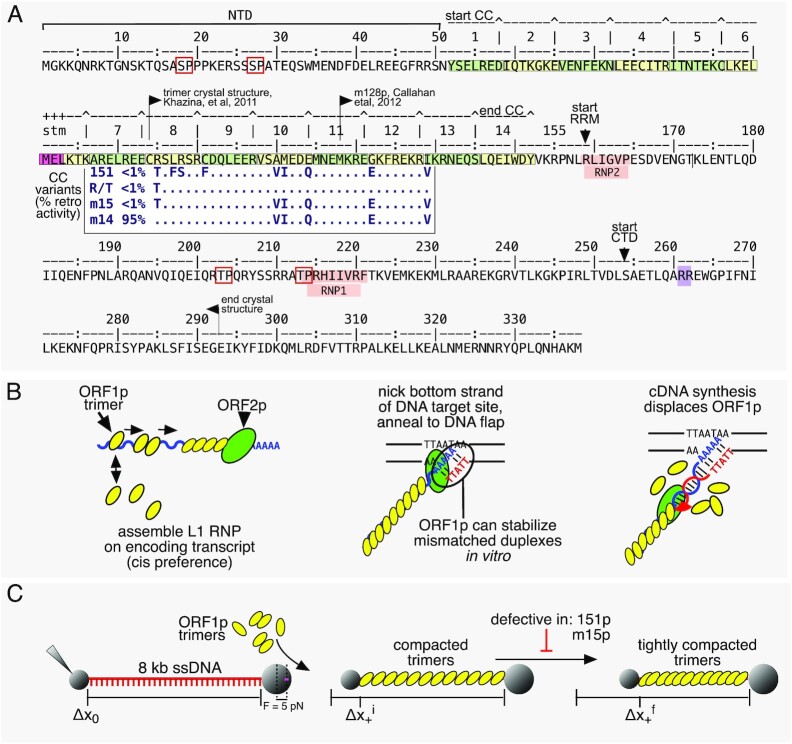
Figure 1.
ORF1p. (A) Annotated sequence of ORF1p showing conserved phosphorylation sites (red boxes), the 14 heptads of the CC (alternating green and yellow boxes with a stammer (stm) in heptad 6), the highly conserved non-canonical RNA recognition motif (RRM), and C-terminal domain (CTD) that contains sequences (notably R261, R262) involved in NA-binding and chaperone activity. The N terminal domain (NTD) and terminal 46 amino acids of the CTD are intrinsically disordered (see text). The insert shows the relevant part of the alignment of the CC variants and their % retro(transposition) activity relative to the 111 (L1Pa1) wild type protein (adapted from Figure 1 in ref. 12). The amino acids that differentiate the coiled coil variants from 111p are their ancestral counterparts in the resuscitated L1Pa5 family (32). (B) Depiction of L1RNP assembly, involvement in, and fate during retrotransposition. (C) Depiction of an ssNA tethered between two beads and its length Δx0, before and after its initial Δx+i and final Δx+f compaction.