Figure 3.
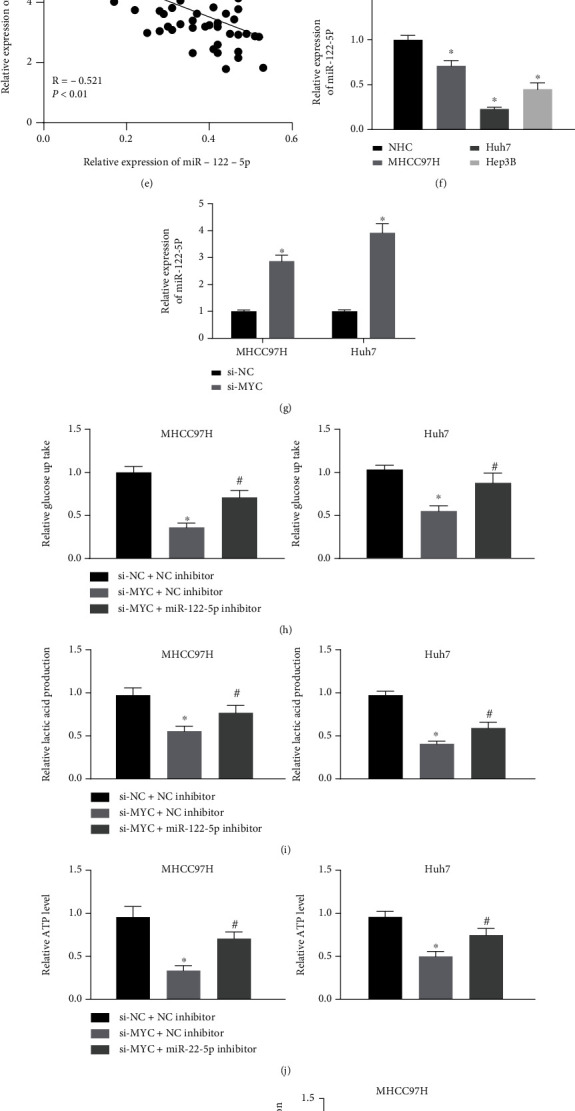
MYC enhances glycolysis in HCC cells by interacting with miR-122-5p. (a) Screening of miR-122-5p upstream factors on the bioinformatics website. (b) Detection of MYC binding to miR-122-5p promoter examined using ChIP. (c) Detection of the miR-122-5p expression in clinical tissues using RT-qPCR. (d) The correlation between miR-122-5p expression and survival of patients with HCC. (e) The correlation between miR-122-5p and MYC expression in HCC tissues. (f) The miR-122-5p expression in NHC and HCC cells by RT-qPCR. (g) Detection of the miR-122-5p expression by RT-qPCR after depletion of MYC in MHCC97H and Huh7 cells. (h)–(j) The changes in glucose consumption (h), lactate production (i), and ATP contents (j) in MHCC97H and Huh7 cells assessed by their respective kits. (k) The protein expression of HK1 and HK2 in MHCC97H and Huh7 cells evaluated using Western blot. ∗p < 0.05 vs. IgG, NHC cells, si-NC, or si-NC + NC inhibitor; #p < 0.05 vs. si-MYC + NC inhibitor. Statistical results were presented by mean ± SD. Paired t-test and one-way or two-way ANOVA were used for comparisons. Each reaction was run in triplicate.
