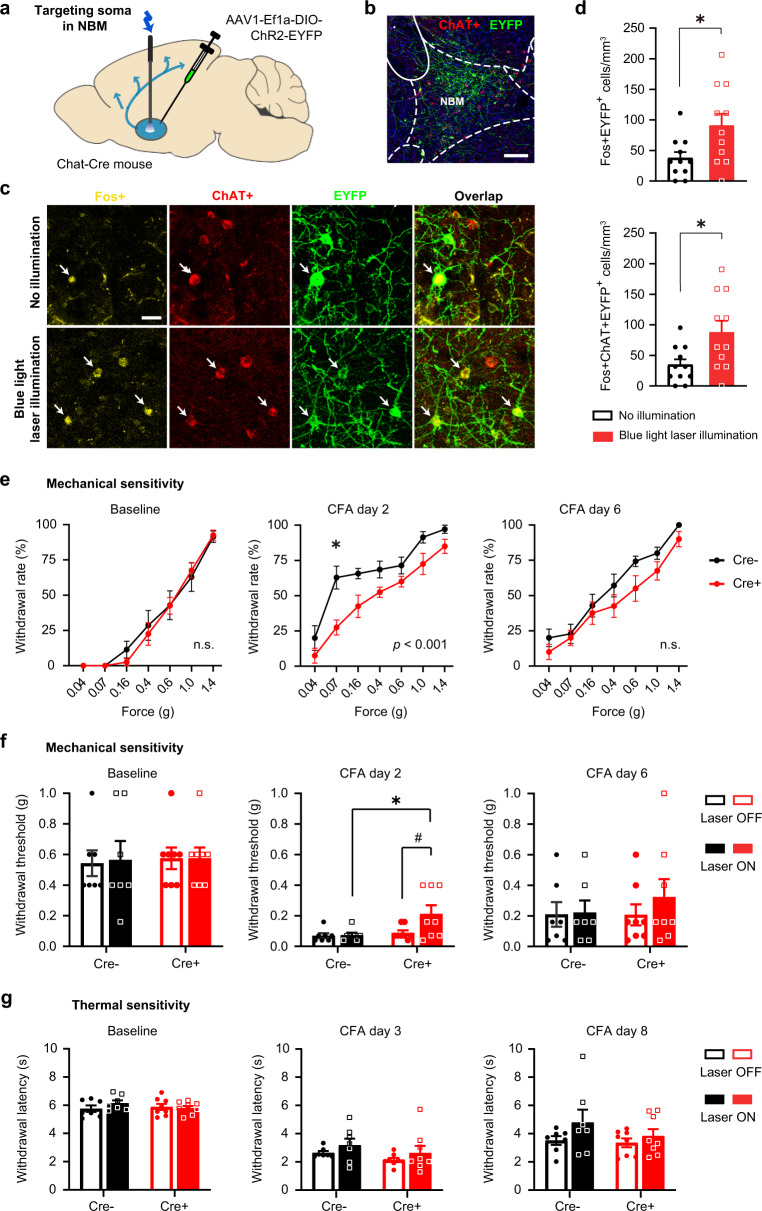
Fig. 4. Optogenetic activation of the NBM cholinergic neurons attenuates inflammatory mechanical, but not thermal, hypersensitivity.
a Scheme for optogenetically manipulating NBM cholinergic neurons with blue laser light. b–d Expression of the excitatory opsin, Channelrhodopsin-EYFP in the NBM (b), typical examples (c) and quantification (d) of enhanced Fos expression in EYFP+ and ChAT+ neurons (arrows in c) with blue light, thus validating the efficacy of optogenetic activation in vivo. n = 3 mice/group; *P < 0.05 (0.0234, top; 0.0183, bottom), unpaired two-tailed t test. Scale bar = 200 µm in b and 25 µm in c. e, f Significant attenuation of peak mechanical hypersensitivity (day 2) induced by intraplantar CFA injection, shown as stimulus–response curves (e) and withdrawal thresholds (f) in response to von Frey stimulation; P values in inset represent ANOVA-based comparison of the two entire stimulus–response curves. g Lack of modulation of hypersensitivity to a heat ramp. e, f n = 7 ChAT-Cre- and 8 ChAT-Cre+ mice; P < 0.05 (*0.0275, middle in e; *0.0139, #0.0231, middle in f), two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Data are presented as mean +/− SEM.