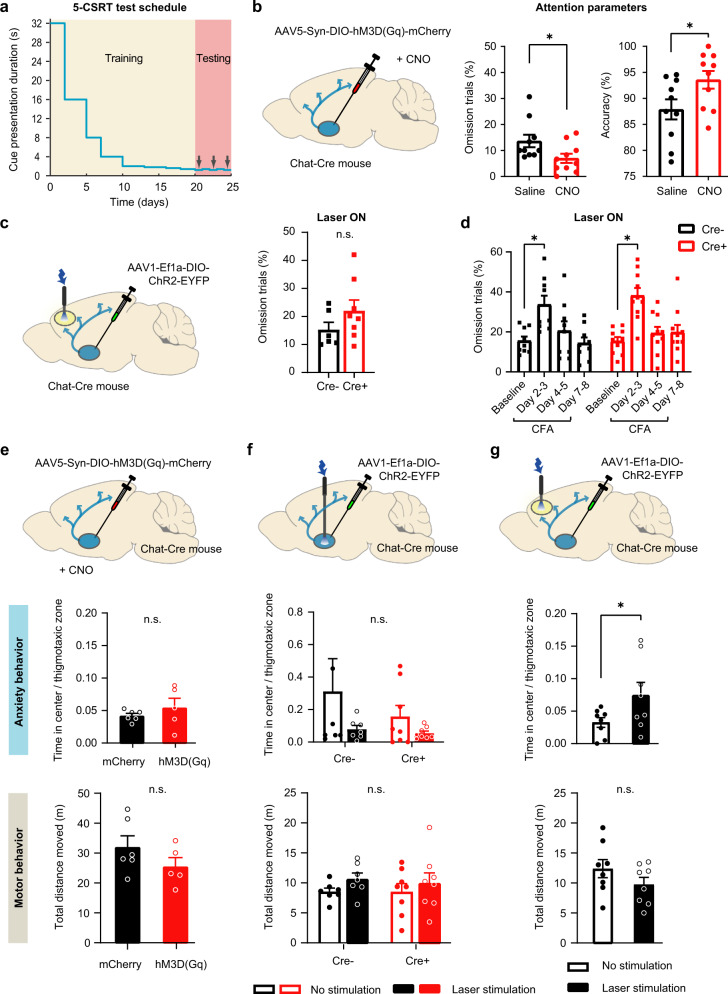
Fig. 7. Analysis of attention, anxiety and motor function in mice with diverse manipulations of NBM cholinergic neurons.
a Scheme of training mice in attention-related tasks in the 5-Choice Serial Reaction Task test (5-CSRT). b, c Increased attention-related parameters in mice with chemogenetic activation of cholinergic neurons in the NBM (b), but not in mice with optogenetic activation of the NBM cholinergic projections to the PL (c). n = 10 mice/group (b); n = 6 ChAT-Cre- and 8 ChAT-Cre+ mice (c); *P < 0.05 (omission trials, 0.0259; accuracy, 0.0008), paired two-tailed t test. d Alterations in attentional behavior upon induction of inflammatory pain-like behavior following hindpaw CFA injection as compared to baseline behavior in presence of blue light stimulation of NBM-PL cholinergic projections in ChAT-Cre+ mice and Cre- control mice. N = 9 ChAT-Cre- and 10 ChAT-Cre+ mice; *P < 0.05 (Cre-, 0.0068; Cre+, <0.0001), two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. e–g Analysis of anxiety-related behavior (upper in e, f, g) and locomotion (lower in e, f, g) in the open-field test in mice with chemogenetic (e) or optogenetic (f) activation of cholinergic neurons in the NBM or mice with optogenetic activation of the NBM cholinergic projections to the PL (g), as compared to their respective control groups. n = 6 mCherry and 8 hm3D(Gq) mice (e); n = 7 ChAT-Cre- and 8 ChAT-Cre+ mice (f); n = 6 mice/group (g); *P < 0.05 (0.0182 for anxiety score in g), two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Data are presented as mean +/− SEM.