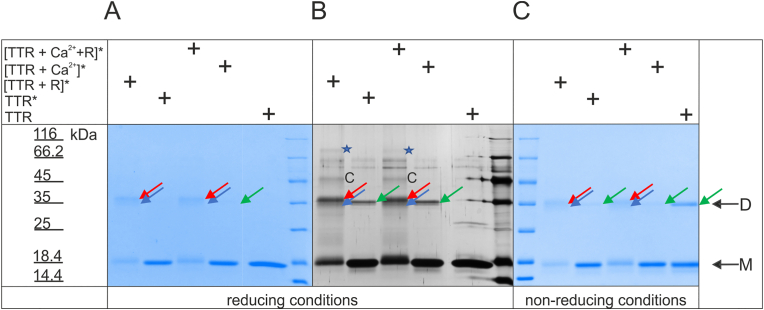
Fig. 6.
An anomalous TTR dimer resistant to dissociation under reducing conditions is formed under riboflavin-sensitized oxidation Samples of TTR (8.7 μM) in HEPES buffer were supplemented with 100 μM riboflavin and/or 100 mM CaCl2 (final concentrations) as indicated and were irradiated at 23 °C for 30 min using an excitation wavelength of 445 nm and slits of 2.0 nm. Then, the samples were incubated overnight at 60 °C, and 50 μg (100 μL) of each sample was applied to a Superdex S75 Increase column. Thirty microliters of TTR peak fraction of each sample eluted from the column with Tris buffer was mixed with four times concentrated sample buffer supplemented with (A and B) and devoid of (C) 2.5% β-mercaptoethanol. Then, the samples were subjected to heat denaturation at 95 °C for 20 min (A and B) or at 95 °C for 15 min, except for the untreated TTR sample, which was denatured at 85 °C for 30 min (C). The gels were run in a Laemmli buffer system and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 (A and C) and silver (B). The arrows indicate anomalous dimer (red), dimer (green) and truncated dimer (blue). C and blue asterisks indicate the conformer and the oligomeric forms of TTR, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)