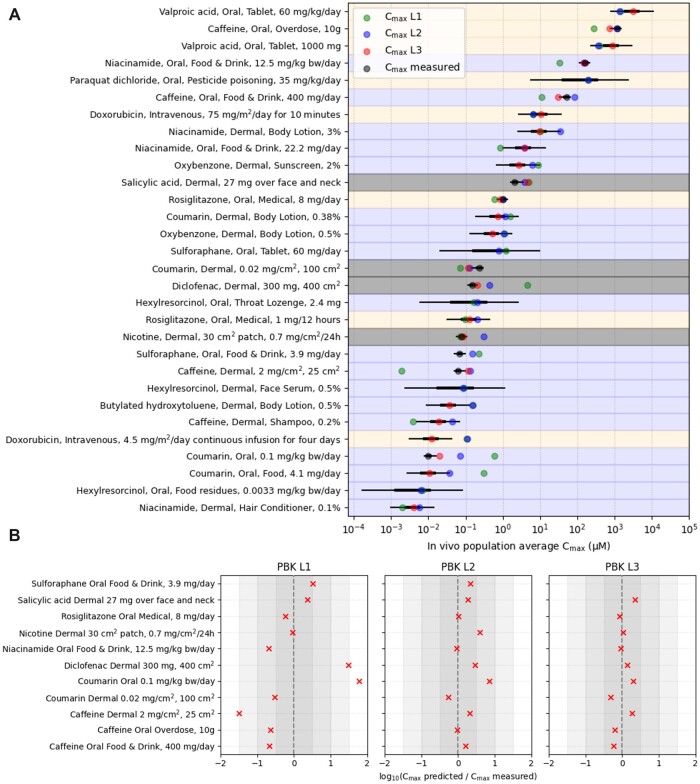
Figure 3.
Overview of the physiologically based kinetic (PBK) model estimates and Cmax error distribution model results. A, Distributions representing the uncertainty of the population average Cmax, conditional on all available exposure information, for all exposure scenarios used to train the Cmax error distribution model. Thin lines cover a centered 95% interval and thick lines a 50% interval of the distribution. The distribution variance is smallest when the measured Cmax is available for the exposure scenario (gray points). The variance is largest when only L1 and L2 PBK estimates are available (green and blue, respectively). Background colors indicate the risk category for each benchmark chemical-exposure scenario assigned at stage 1 (blue—low, orange—high). The 4 dermal exposure scenarios from Li et al. (2022) (used only for training the Bayesian model) are indicated in gray. B, A comparison between Cmax PBK estimates at different parameterization levels and the corresponding measured Cmax values (for the 11 exposure scenarios where these values were available), provided in terms of a ratio between estimated and measured Cmax (red crosses). The shading indicates how far the ratio is from 1 (given by the vertical dashed line). Crosses to the left of the dashed line correspond to Cmax values that were underpredicted by the PBK models, whereas to crosses to the right correspond to values that were overpredicted.