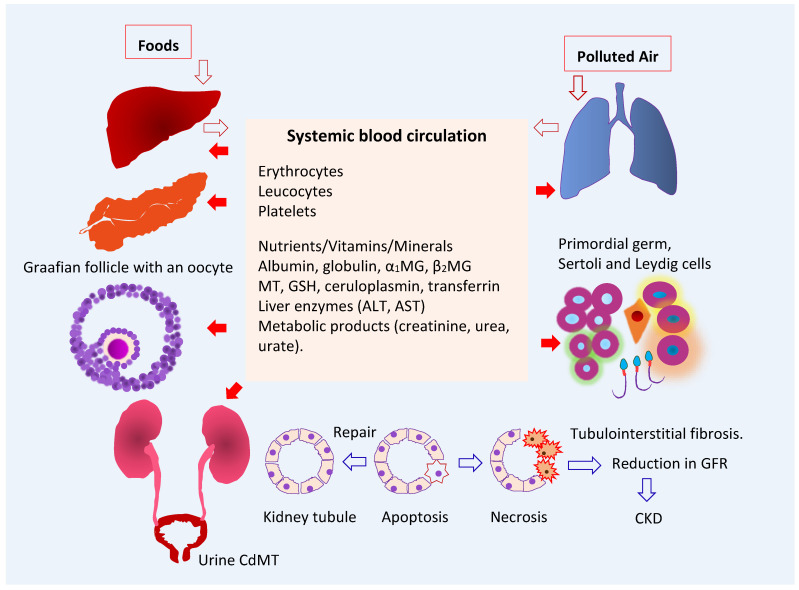
Figure 1.
Multiple toxicity targets of cadmium. Ingested Cd is absorbed and transported to liver, where synthesis of MT is induced, and CdMT is formed. The fraction of absorbed Cd not taken up by hepatocytes in the first pass reaches systemic circulation and is taken up and accumulated by cells throughout the body. After glomerular filtration, CdMT is reabsorbed by kidney tubular cells. Other forms of filtered Cd can be reabsorbed by the kidney nephron transporters for iron, zinc, manganese, and calcium. Abbreviations: Cd—cadmium; MT—metallothionein; CdMT—cadmium-metallothionein complex; α1MG—α1-microgloulin; β2MG—β2-microglobulin; GSH—glutathione; ALT—alanine aminotransferase; AST—aspartate aminotransferase; GFR—glomerular filtration rate; CKD—chronic kidney disease.