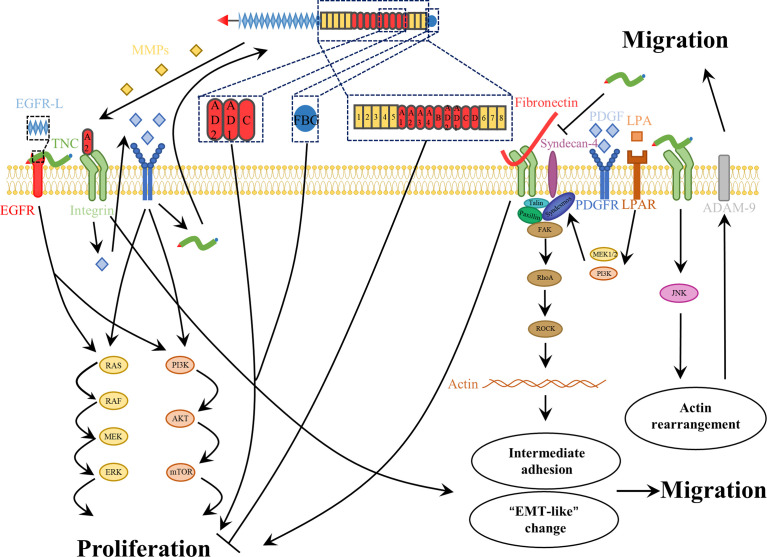
Figure 4.
The roles of TNC in glioma cell proliferation and migration. For one thing, the role of TNC in glioma cell proliferation is complex. The EGF-like repeats, the FBG region, A2 and some alternatively spliced domains, such as AD1, -AD2 and -C, of TNC as well as integral TNC molecule contribute to the glioma cell proliferation. In contrast, the fragment composed of all FNIII-domains decreases the proliferation of glioma cell. In addition, TNC impairs the adhesive properties of FN, which contributes to glioma cell proliferation. For another thing, TNC promotes glioma cell invasiveness. This molecule not only contributes to the intermediate adhesion that support cell motility, but also promotes “EMT-like” changes. Moreover, TNC also induces matrix destructing enzymes to promote tumor cell migration.