Figure 1. mir-35 decay is seed-sequence dependent.
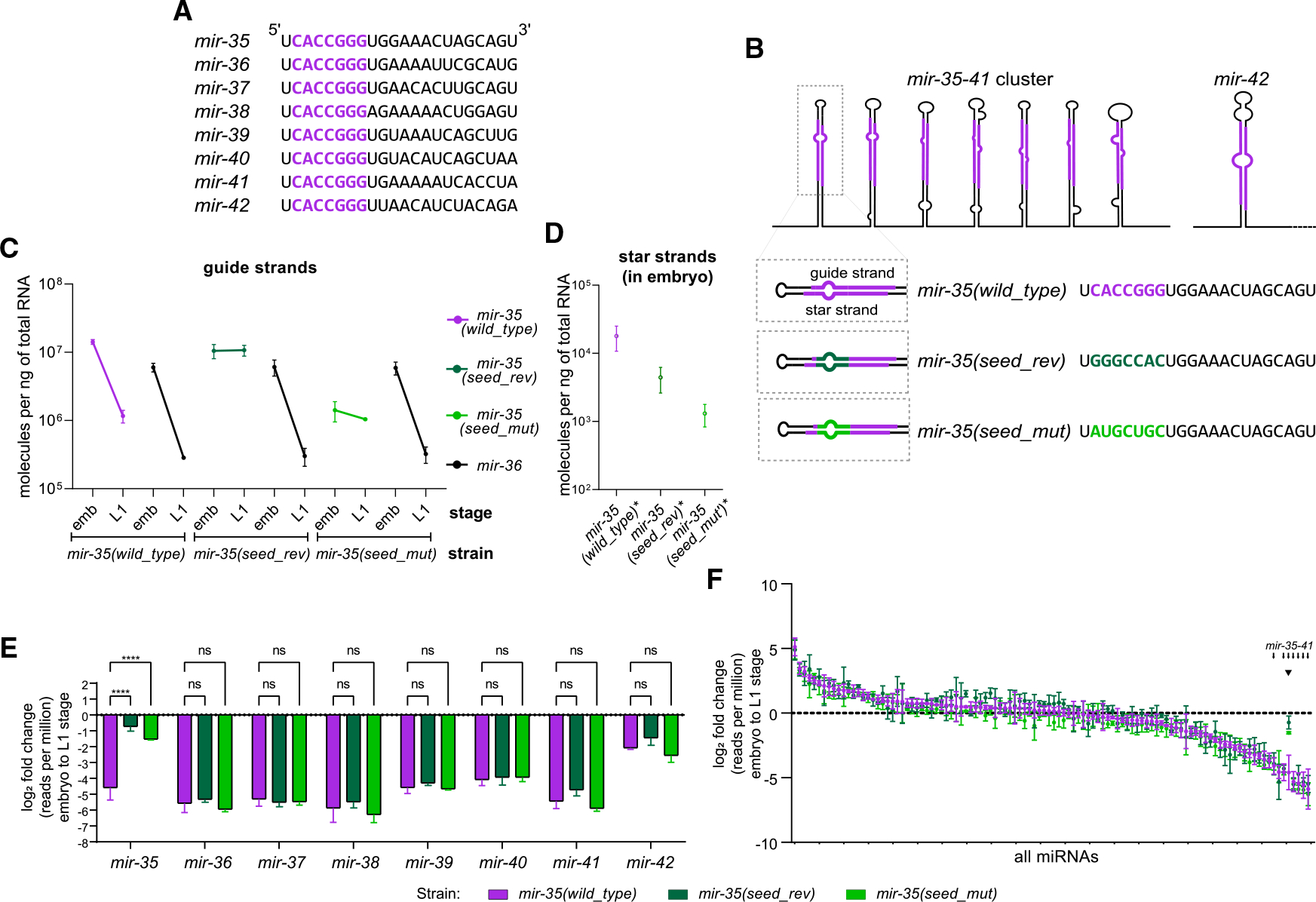
(A) Sequences of mir-35–42. Seed sequence in purple.
(B) Schematic of the mir-35–41 cluster and mir-42 with sequences of mir-35 and variants.
(C and D) Absolute quantification of mir-35 and mir-36 guide strands (C) or star strands (D).
(E and F) Log2(fold change) from embryo to L1, calculated from deep sequencing for either the mir-35–42 family (E) or all miRNAs >50 RPM in wild type (F). Note that color of bar indicates strain, not necessarily a mutant miRNA; only mir-35 is mutated in the indicated mutant strains.
(E) Two-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. ****p value < 0.0001.
(F) Small arrows indicate positions of mir-35–41 on ranked x axis, and arrowhead indicates mir-35 and mutant variants.
(C–F) Mean and SEM of three biological replicates are shown.
