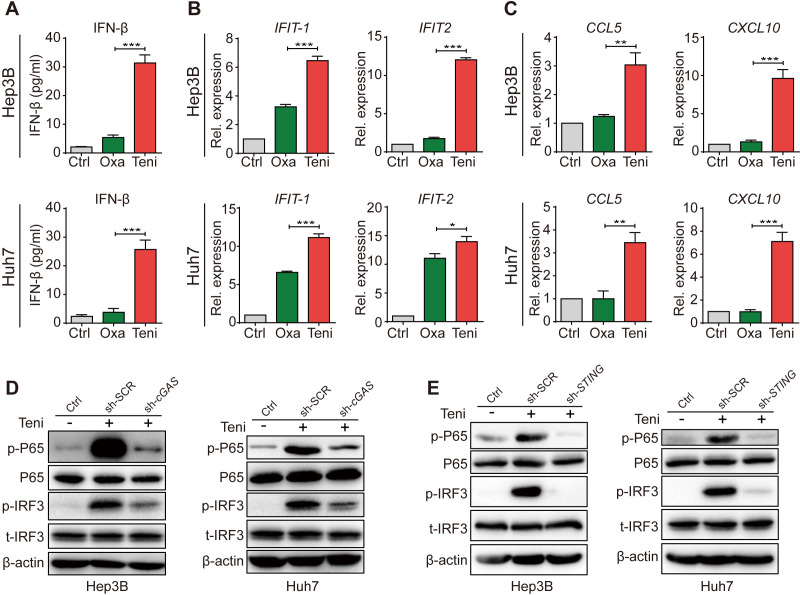
Figure 1.
Teniposide triggered type Ⅰ interferon and NF-κB signaling through the cGAS-STING activation in human HCC cells. (A–C) Hep3B and Huh7 cells were treated with oxaliplatin or teniposide at each IC50 for 24 hours and the supernatant IFN-β was then measured by ELISA (A) and the mRNA expression of IFIT-1 and IFIT-2 (B) and CCL5 and CXCL10 (C) was measured by RT-qPCR. (D) Hep3B and Huh7 cells transduced with cGAS-shRNA or scramble-shRNA were treated with teniposide at each IC50 for 24 hours and the cellular protein expression of p-IRF3 and p-P65 was then detected by immunoblotting; β-actin was used as a loading control. (E) Hep3B and Huh7 cells transduced with STING-shRNA or scramble-shRNA were treated as in (D) and the cellular protein expression of p-IRF3 and p-P65 was then detected by immunoblotting. Data in (D) and (E) are representative of three independent experiments. Data in (A), (B) and (C) are shown as mean±SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. cGAS-STING, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes; Ctrl, control; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; IFN-β, interferon β; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; Oxa, oxaliplatin; Rel. expression, relative expression;RT-qPCR, real time quantitative PCR; sh-SCR, short hairpin RNA-scrambled; sh-cGAS, short hairpin RNA-cGAS; Teni, teniposide.