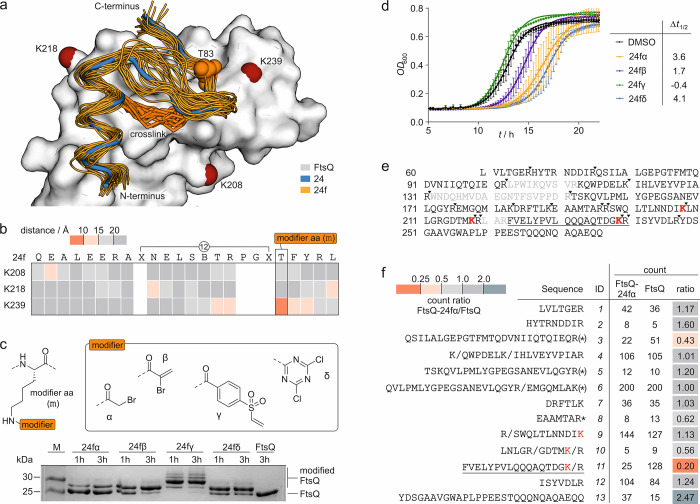
Figure 2.
(a) Overlay of peptide 24 (blue, crystal structure, PDB: 6h9o) bound to FtsQ (white) with binding poses of 24f (orange) derived from MD simulations (snapshots every 10 ns from three independent 100 ns simulations; the pdb file with atomic coordinates is provided in the Supporting Information). The cross-links in 24f (orange stick representation) and FtsQ lysine residues in proximity to the binding site (d̅ < 15 Å, red spheres for Nε) are highlighted. (b) Heat map of the average distance between the Nε of the selected lysine and the Cβ of 24f residues over a 400 ns MD simulation (Table S2). (c) Top: structure of the four selected modifiers (α, β, γ, and δ) installed in a modified amino acid (m), which was introduced at position T83 of 24f. Bottom: 17% Tris/Tricine PAGE (protein modification assay) assessing peptide binding to FtsQ(50–276). Covalent inhibitors 24fα–δ (c = 125 μM; for peptide details, see Table S3) were incubated with FtsQ(50–276) (c = 50 μM) for 1 or 3 h. Up-shifted bands are indicative of modified FtsQ. (d) Growth assay using E. colilptD4213 (imp) after treatment with inhibitors 24fα–δ (c = 50 μM). Optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was measured every 15 min over 22 h. Measurements were conducted in triplicate (n = 3 technical replicates, error bars = SD). (e) Sequence coverage for unmodified FtsQ(50–276) after tryptic digest in the MS/MS experiment (only sequence fragments with a count of >1 were included, and missing sequence fragments are shown in gray; the solid inverted triangle indicates the protease cleavage site). (f) List of identified sequences (count of >1). Counts for 24fα-modified and unmodified FtsQ as well as the corresponding count ratio are shown (* oxidized methionine, (*) oxidized and non-oxidized methionine, / additional cleavage site; for full list of fragments, see Table S4).