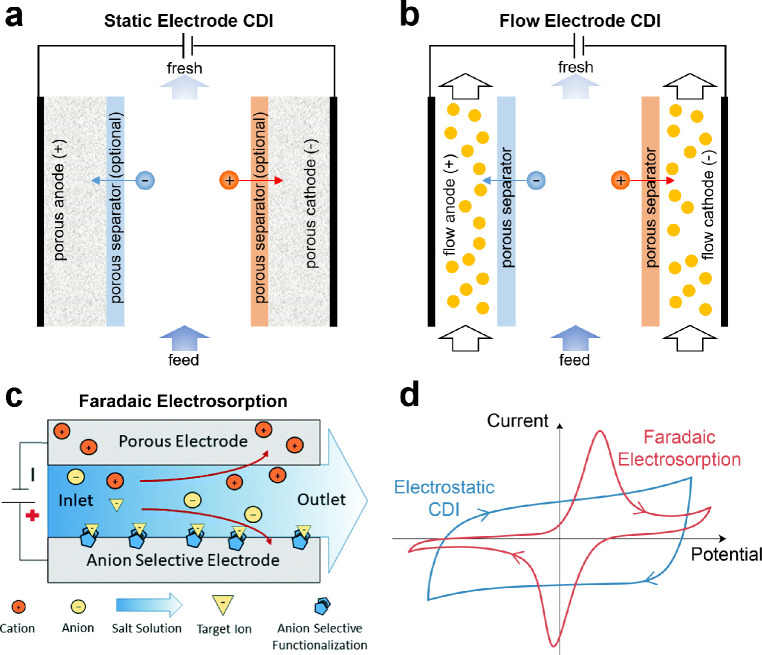
Figure 20.
Schematics of various electrosorption processes. (a) Static electrode CDI has electrodes that are rigid solids, such as porous carbon and intercalation materials, whereas (b) flow electrode CDI has electrodes that are made of a suspension (or slurry) of carbon beads in an electrolyte. When oriented vertically, FCDI is often referred to as fluidized bed CDI, in which the flow of suspended carbon is impeded by gravity to establish a densely packed fluidized bed. (c) Faradaic electrosorption comprises redox-active electrodes that can selectively remove target ions. Reproduced with permission from ref (646). Copyright 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry. (d) Typical cyclic voltammograms for electrostatic electrosorption, where double-layer charging is associated with relatively constant capacitance over a wide range of potentials, versus Faradaic electrosorption (or electrochemical adsorption), where redox reactions that transfer electrons between certain ions and the electrode yield peaks in the voltammogram at specific potentials.