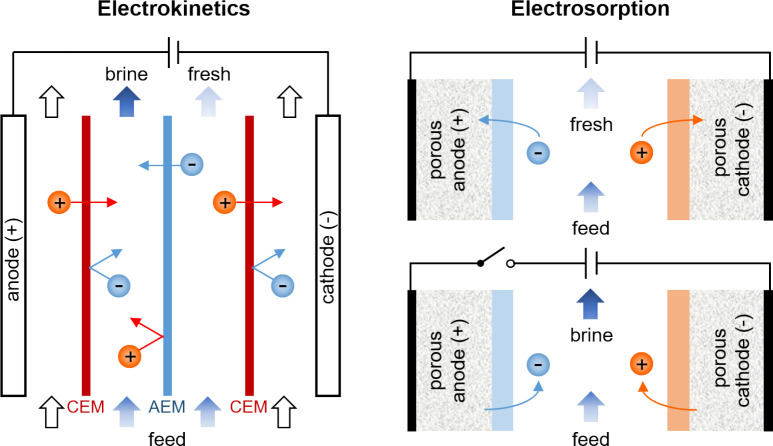
Figure 3.
Electrokinetics and electrosorption are the two main mechanisms by which contaminants are separated in any nondestructive electrochemical process. Electrokinetic processes, which are typically continuous, involve transport of charged or uncharged but dielectric119,120 species in an electrolyte in response to an applied electric field, and so removal of contaminants relies on effective mass transfer. Electrokinetic methods like EDI and shock ED use porous materials in the feed channels to increase ion removal and improve energy efficiency when the feed is dilute. Electrosorption processes are cyclic and encompass all phenomena in which the binding of contaminants is aided by an applied electric field. In addition to effective transport, electrosorption relies on favorable reaction kinetics and thermodynamics.