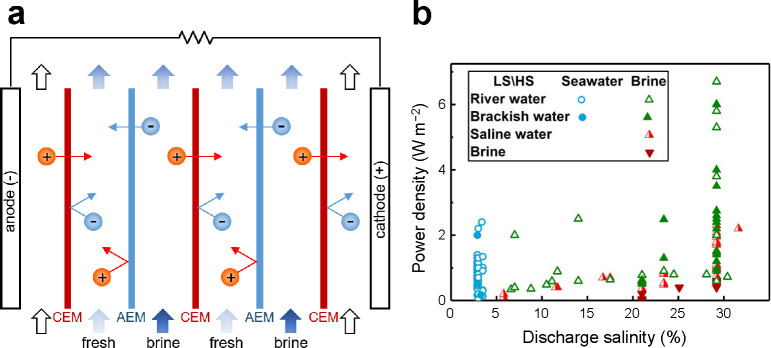
Figure 39.
Operating principles and empirical results of reverse ED. (a) Dilute and concentrated streams are passed through a stack of alternating AEMs and CEMs. Differences in the chemical potentials of adjacent streams generate an electric potential across each membrane, and the total voltage is the sum of the potential differences across each membrane. In most reverse ED systems, reversible redox couples (e.g., Fe2+/Fe3+, [Fe(CN)6]4–/[Fe(CN)6]3–) in a supporting electrolyte (e.g., NaCl–HCl) are used as electrode streams to convert ion flux into electrical current.1066−1068 (b) Power density versus discharge salinity for various pairs of low salinity (LS) and high salinity (HS) feeds. Reproduced with permission from ref (1069). Copyright 2018 Elsevier.