Figure 6.
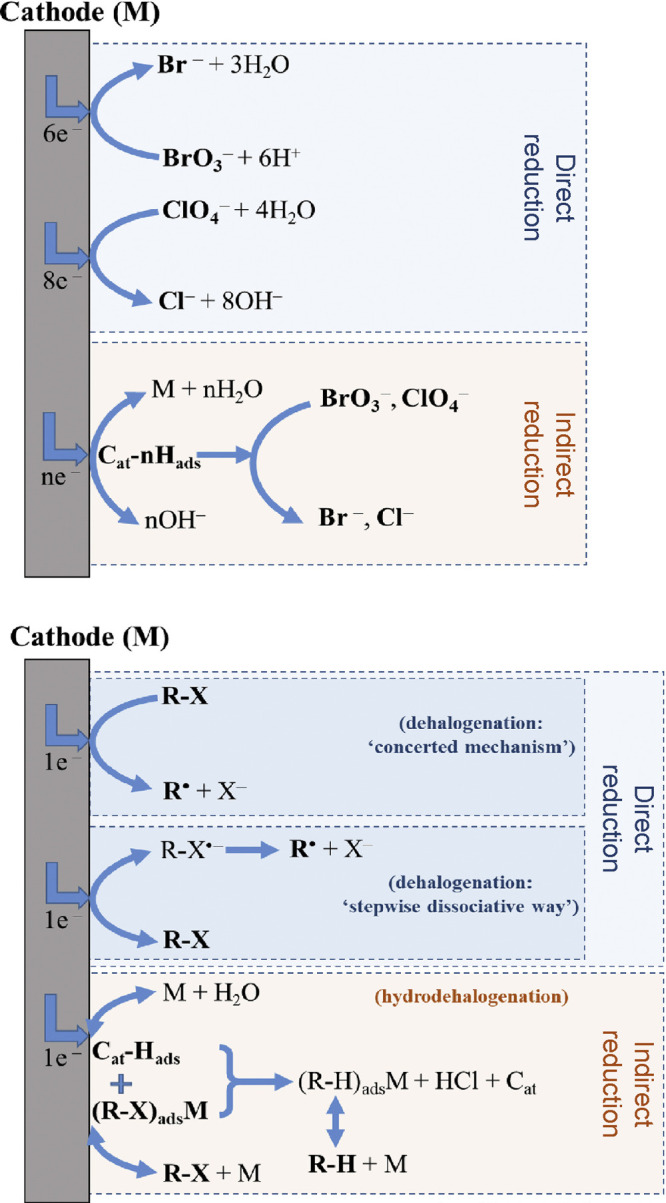
Electrochemical reduction is an established conversion method that is used to treat oxidized contaminants, such as (top) inorganic and (bottom) organic halides (R-X). The method involves formation of high energy electrons or reactive species that interact with contaminants either at the cathode surface (direct reduction) or in the bulk (indirect reduction). M refers to the cathode material (i.e., the catalyst, Cat); Cat-Hads, (R-X)adsM, and (R-H)adsM are the hydrogen atom, organic halide, and dehalogenated organic compound (R-H), respectively, adsorbed on the cathode. Reproduced with permission from ref (98). Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
