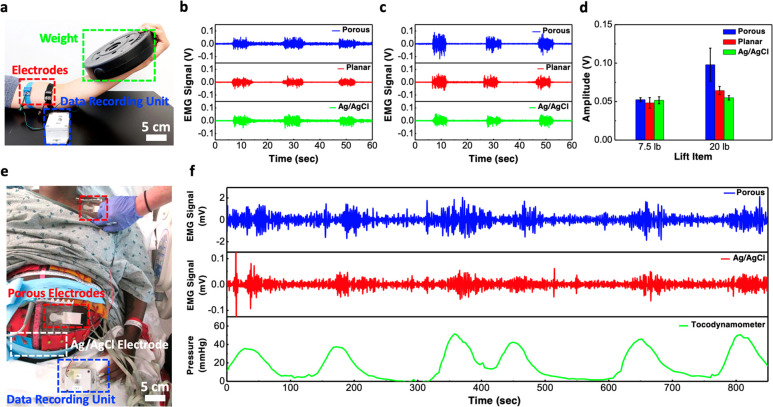
Figure 5.
EMG signal recording from skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. (a) Photograph showing the setup for measuring EMG signal from the contraction of biceps. (b, c) EMG signals measured using various kinds of electrodes when the subject was lifting a (b) 7.5-lb or (c) 20-lb weight. (d) Comparison of the EMG signal amplitude measured with sponge, planar, and commercial Ag/AgCl electrodes. (e) Photograph showing the setup for recording EMG signals from uterine contraction activities in a clinical setting. (f) Comparison of EMG waveforms recorded from our porous electrodes and in-house built data recorder, the commercial BioSemi active Ag/AgCl electrodes and BioSemi biopotential measurement system and the corresponding uterine contractions recorded from a tocodynamometer.