Figure 8.
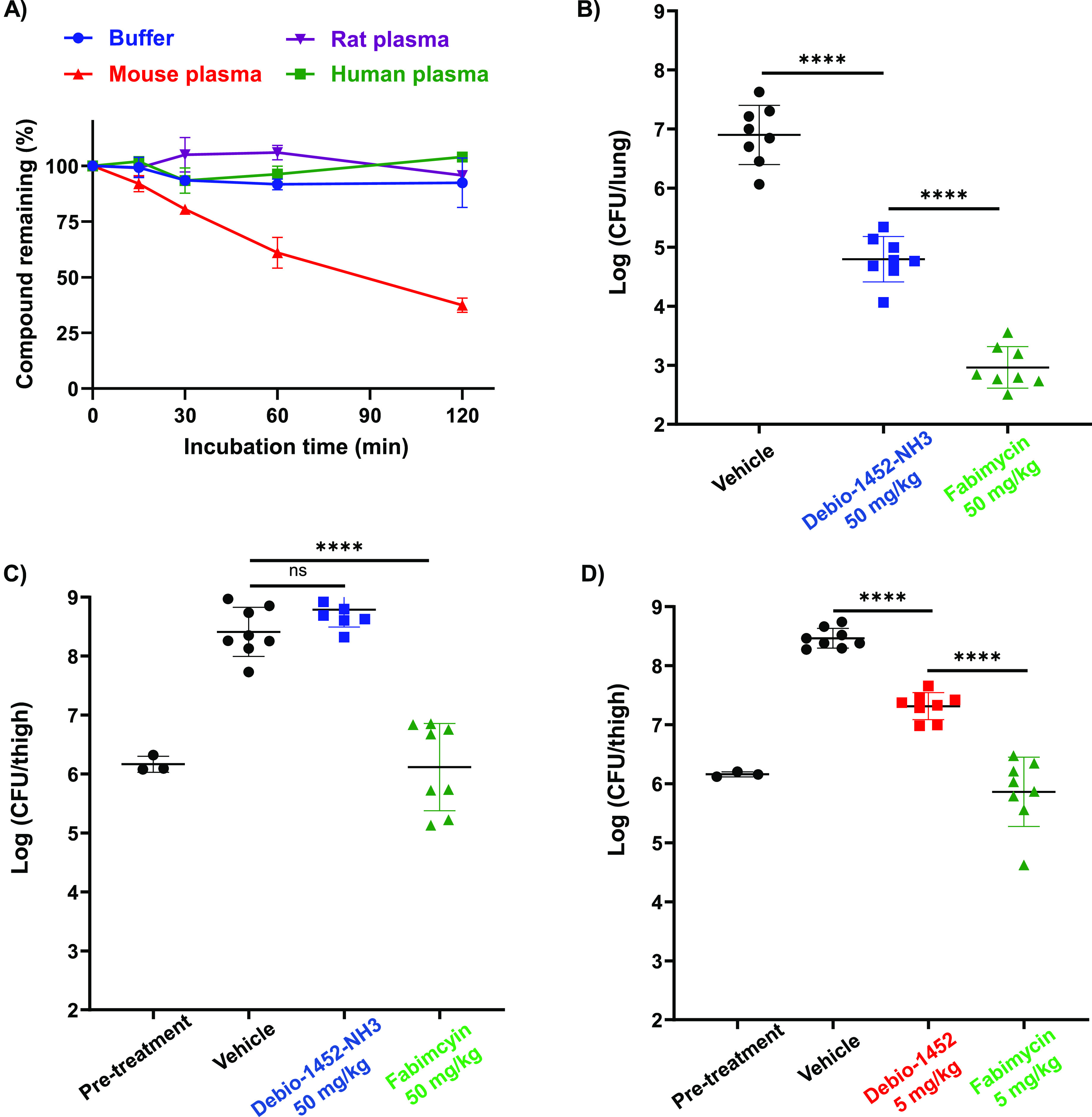
Plasma stability and in vivo efficacy of fabimycin. (A) Assessment of fabimycin stability in plasma. Data shown as the mean and standard deviation from two experiments. (B) Acute pneumonia infections initiated in CD-1 mice with A. baumannii AR-0299 (1.6 × 108 CFUs per mouse intranasally). Mice were treated with vehicle (8 mice) or FabI inhibitor (8 mice per group) 4, 23, and 41 h postinfection (50 mg/kg intramuscular) and the bacterial burden evaluated at 48h postinfection. (C) Neutropenic mouse thigh infection initiated in CD-1 mice with A. baumannii AR-0299 (1.22 × 106 CFUs per mouse intramuscular in thigh) were treated with vehicle (8 mice) or FabI inhibitor (8 mice per group) 2, 6, and 11 h postinfection (50 mg/kg intramuscular), and the bacterial burden was evaluated 26h postinfection. (D) Neutropenic mouse thigh infection initiated in CD-1 mice with S. aureus USA300 LAC (2.3 × 106 CFU per mouse intramuscular in thigh) were treated with vehicle (eight mice) or FabI inhibitor (eight mice per group) 2 and 7 h postinfection (5 mg/kg retro-orbital IV), and the bacterial burden was evaluated 24 h postinfection. Debio-1452-tosylate used. FabI inhibitors formulated with 20% SBE-β-CD in H2O. In B, C, and D statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. NS, not significant. ****P < 0.0001. Error bars represent standard deviation.
